
A personal statement for graduate school is essential for an application that offers candidates the chance to showcase their abilities, experiences, and aspirations in a thoughtful and compelling manner. A personal statement generally focuses more on the applicant’s academic and professional goals, displaying their suitability for advanced study in their desired field. Candidates can articulate why they are interested in the certain program, account for their experiences, and how they may contribute to the program. This article provides a step-by-step guide.
Definition: Personal statement
In a personal statement, you write a short essay of about 1,500 to 3,000 words. This essay tells a compelling story about yourself, your motivations, and why you’re placing an application. You should demonstrate the following three things when writing a successful personal statement:
- Your personality: Who are you? What are your motivations, interests, and values?
- Your goals: What do you hope to gain from the program?
- Your talents: What talents will you bring to the program? How will the program help you advance?
When applying for a graduate program, don’t just summarize who you are or your achievements. Instead, write a compelling narrative about yourself and your achievements in your voice.
How to get started with your statement
Before writing a personal statement, understand the application’s requirements and respond directly to the questions or prompts.
Introduction of a personal statement
The first paragraph of a personal statement is the introduction, and it should hook your readers. The introduction sets the tone, smoothly leading into your story.
Option 1: Start with a specific scene
A compelling way to catch your reader’s attention is to set up a specific scene that says something about your interests and character. Start with an intriguing sentence, pull the reader in and create a convincing and confident atmosphere.
Here are some topics to help you get started:
- A personal perspective or a life-changing experience
- A family history
- A teaching or learning experience
- An unexpected and impacting encounter
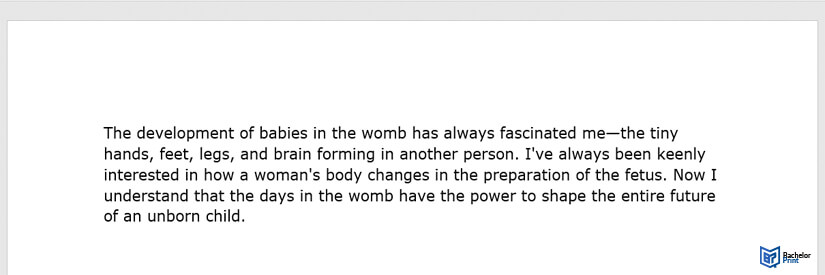
The following illustrates an example:

Option 2: Start accounting for your motivations
Talking about your motivations in a personal statement shows your commitment and enthusiasm for the program you’re applying for. Stating your interests is okay, but emphasizing why you’re interested is even better.
Some topics here could include:
- Recent discoveries or long-lasting interests
- Hard-earned or natural interest
- The role it plays in other life aspects
- How it contributes to society
The following illustrates an example:
Dos and don’ts of an introduction
The followings are some dos and don’ts of an introduction in a personal statement:
Dos
- Save your introduction for last. If you need help starting your introduction, you can set it aside.
Don´ts
- Don’t start with a cliché, e.g., I have loved soccer for as long as I remember… or ever since I was in high school…
Body of a personal statement
Once you know the topics of your personal statement, start writing about your motivations and experiences in detail. You can use some of the strategies outlined below:
Option 1: Personal development
Focus on your personal growth and development in the body section of a personal statement. Only include some things about yourself; write what’s relevant to your application. Craft an exciting narrative that tells how you’ve changed and actively undergone self-growth.
It’s crucial to consider the following when applying for graduate school:
- How the school or course sparks interest
- How the surroundings contribute to the growth and development of skill sets and knowledge
- Your next step and how the school or course fits into your plans
The following illustrates an example:

Option 2: Take advantage of obstacles on your path
You could turn this into strength if you’ve had a rough transition into graduate school. Your personal statement can tell your story of overcoming obstacles in your path. Try focusing on the positive part of your story and putting less gravity on the negatives.
Characteristics like resourcefulness, resilience, and perseverance are qualities that make a promising graduate school candidate. Some obstacles may include the following:
- The social, cultural, or economic background undermined in the subject or career path.
- In the case of gaps in the resume or under-average grades, refer to obstacles and struggles conquered.
The following illustrates an example:

Option 3: Illustrate relevant skillset and knowledge
You can show familiarity with your chosen subject and the department by writing a personal statement for a PhD or other research-based program. Please focus on the subject you wish to specialize in and reflect on why it’s essential.
Consider the following when using this approach:
- Reflect on the subject or topics that are relevant and that you’ve been specializing in during your studies.
- Draw attention to relevant academic milestones, teachers that made an impact, or other relevant highlights during your studies.
- Emphasize questions that arose during your research and that you’re interested in studying.
The following illustrates an example:

Option 4: Professional ambitions and concrete goals
When applying for a professionally-based program like an MBA, focus on your goals and ambitions. Explain how the program will help you achieve your ambitions in the body of your personal statement. Most importantly, demonstrate that you’ve put much thought into your career and explain how the program best suits your chosen profession.
Some factors to consider during this process include the following:
- Focus on your character and how it fits the professionally oriented program. How is graduate school giving you the space to grow?
- Demonstrate your past experience in the specific field and include your accomplishments and how you may develop further.
- In the case of a career change, explain your decision and how your experience may support your success.
The following illustrates an example:

Dos and don’ts of a body
Some dos and don’ts of a body section in a personal statement include:
Dos
- Make all your statements into compelling stories.
- Reflect, relate and evaluate your experiences in broader themes.
Don´ts
- Don’t rehash your resume by noting down every achievement.
- Don’t ignore or forget the prompt throughout the paper.
Conclusion of a personal statement
The conclusion should bring the reader back to your program of study. It would help if you highlighted what you hope to achieve from the program. Be clear if it’s exploring philosophical questions, gaining skills, or both.
Emphasize why you’re the best candidate for this program and why the program is ideal for helping you achieve your goals. You can do this by answering the following questions:
Option 1: What are you aspiring after?
If you’re applying for an academic research-based or academic program, try ending with a curious conclusion. This can be something that you’re aspiring to learn and why you think the program is ideal. This is the best place to show your enthusiasm if there are some faculty members that you aspire to learn from.
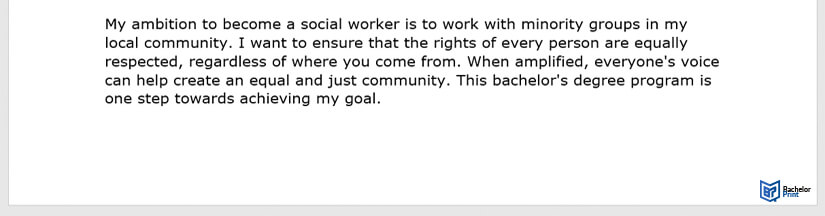
The following illustrates an example:

Option 2: What do you want to do?
If you apply for a more professional training-oriented program, your conclusion may lean towards stating your career aspirations. You can answer the roles you’ll play in society and why the program is a good fit.
The following illustrates an example:
Dos and don’ts of a conclusion
Consider the following dos and don’ts of a concluding section in a personal statement:
Dos
- Think bigger than yourself, your community, society, and the academic field.
- Focus on using the knowledge obtained in graduate school in the future.
Don´ts
- Don’t summarize anything you mentioned in your personal statement.
- Don’t add new information that should be in the introduction.
Personal statement: Editing and proofreading
Your personal statement is the first impression you’ll give the recruiter; hence, revise and polish your work. You don’t have to be too formal, but your voice should stand out and be clear, coherent, and direct. Ensure your paragraphs connect, so use transitions and topic sentences to create clear connections between the paragraphs.
Rewrite your statement as much as you deem necessary. Personal statements have lots of freedom, so experiment and move information around. Lastly, carefully proofread and fix language errors or typos in your work.
Before submitting your work, you can also use an editing tool to:
- Eliminate awkward mistakes
- Correct your grammar
- Strengthen your arguments
FAQs
A statement of purpose is a formal essay focusing on professional and academic goals. A personal statement can be creative and discuss your interests, motivations, and goals.
No. You should craft different statements when applying for multiple graduate programs.
You should discuss your ambitions, personality, and goals. Don’t copy anything online, as plagiarized statements are usually disqualified.
