
Relative pronouns are a fundamental aspect of English grammar, serving as an essential tool in both everyday communication and academic writing. Making use of these pronouns correctly is crucial, as it enhances the clarity, fluidity, and coherence of the text. By linking sentences and providing additional information about the subjects or objects they refer to, relative pronouns help writers construct complex, informative sentences that are vital for expressing detailed ideas and arguments.
Definition: Relative pronouns
Relative pronouns are words used to introduce relative clauses, which are a type of dependent clause, that connect them to nouns or pronouns in an independent clause. These clauses provide additional information about the noun or pronoun, known as the antecedent.
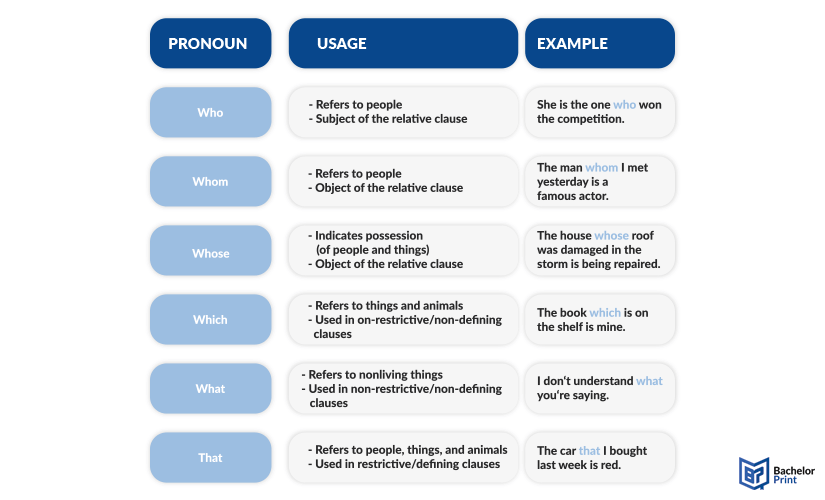
The main relative pronouns in English are “who,” “whom,” “whose,” “which,” and “that.”
- Who: Used for people (as the verb’s subject)
- Whom: Used for people (as the verb’s object)
- Whose: Used for people and things
- Which: Used for things and animals
- That: Used for people, things, and animals
Relative clauses are parts of a sentence that describe or provide extra information about the noun mentioned before them in the sentence. They are directly connected to relative pronouns because they link the clause to the antecedent. There are two types of relative clauses:
- Restrictive/defining clauses (essential to the sentence’s meaning; no comma required)
- Non-restrictive/non-defining clauses (add extra information; comma required)
The antecedent is the word that the relative pronoun refers back to. It’s the “thing,” “person,” or “animal” you’re providing more information about.
“The book” is the antecedent to “that,” and the relative clause “that I read” provides more details about the specific book being talked about in the sentence.
Subject
Object
Possessive
Who
Who/whom
Whose
Which
Which
Whose
That
That
- Subject: The pronoun acts as the subject of the relative clause.
- Object: The pronoun acts as the object of the relative clause.
- Possessive: The pronoun indicates possession to the antecedent.
In essence, relative pronouns serve as the bridge between the main part of the sentence and the additional information provided by the relative clause, making the sentence complete and the meaning clear.
Overview of all relative pronouns
An overview of all relative pronouns provides insight into these essential grammatical tools used in language. Understanding their roles as subjects, objects, or possessives enhances clarity and expression in academic writing as well as everyday speech.
Relative clauses
Relative clauses are sometimes called adjective clauses because they provide additional information about the subject in the independent clause they relate to. They are introduced by relative pronouns, and there are two main types:
- Restrictive relative clauses
- Non-restrictive relative clauses
In these types of clauses, the relative pronoun can be the subject, object, or possessive pronoun.
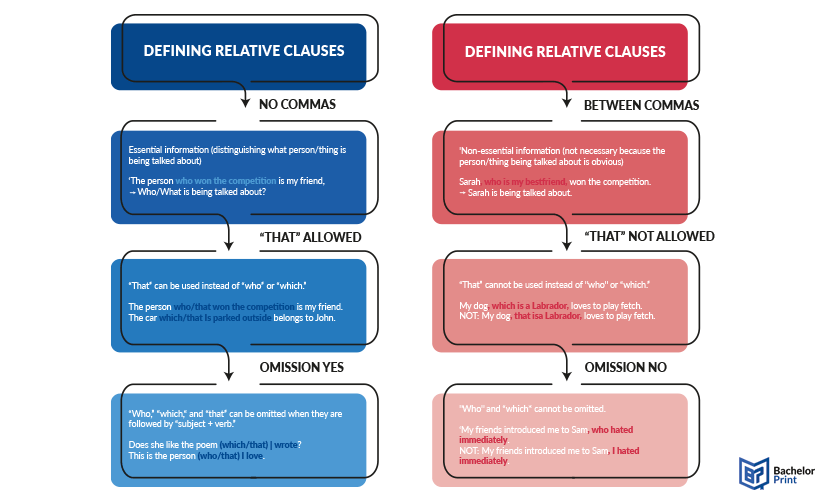
Defining/restrictive relative clauses
Defining/restrictive relative clauses provide essential information to define or identify the noun they modify. They are necessary for the meaning of the sentence because, without them, the sentence would not be clear. These clauses do not have commas separating them from the rest of the sentence.
“That you lent me” provides essential information to identify which specific book is being talked about.
The table below sums up the use of relative pronouns in restrictive clauses.
Function
Subject
Object
Possessive
People
Who, that
That, who, whom
Whose
Things/concepts
Which, that
Which, that
Whose, of which
Place
Where
Time
When
Explanation
What, why
Non-defining/non-restrictive relative clauses
Non-defining/non-restrictive relative clauses add extra information about a noun, but this information is not essential to the sentence’s meaning. The sentence would still be clear and complete without the non-defining relative clause. These clauses are usually set off with commas.
“Who lives in New York” provides additional information that is not essential to identify “my brother” because the speaker has only one brother.
The table below sums up the use of relative pronouns in non-defining clauses.
Function
Subject
Object
Possessive
People
Who
Who, whom
Whose
Things/concepts
Which
Which
Whose, of which
Place
Where
Time
When
Explanation
What, why
Relative pronoun as the subject/object
When the relative pronoun is the subject of the relative clause, it performs the action of the verb within that clause. It refers back to a noun or pronoun mentioned in the main clause and takes the place of the subject in the relative clause. The relative pronoun (who/which/that) directly precedes the verb in the relative clause.
“Who” is the relative pronoun and the subject of the relative clause, so repeating the subject “he” and “they” is not needed!
When the relative pronoun is the object of the relative clause, it receives the actions performed by the subject within that clause. It still refers back to a noun or pronoun in the main clause, but now functions as the object of a verb. It is the recipient of the action, not the one performing it. The relative pronoun (whom/which/that) is followed by the subject (if any) and the verb of the relative clause.
“That” and “whom” are the relative pronouns and the objects of the relative clause, so repeating the subject “it” and “her” is not needed!
Note: No additional subject/object is needed within the relative clause because the relative pronoun fulfills this role.
In the following, we provide a concise comparison between the two kinds of relative clauses. Their differences, like comma placement and replacing pronouns with others, were illustrated by numerous example sentences to help you get a better grasp.
Possessive relative pronouns
Possessive relative pronouns are a subset of relative pronouns used to indicate possession, belonging, or association within a relative clause. They relate the clause to a noun or pronoun mentioned earlier in the sentence, specifying ownership or a similar relationship. In English, the primary possessive relative pronouns are “whose” and “of which.”
- Whose: Used to refer to both people and things, indicating that the noun that follows is in possession of or closely associated with the noun that precedes it. It is used in defining and non-defining relative clauses.
- Of which: More formal and is primarily used to refer to things, not people. It is often used in written English, particularly in formal or academic contexts. The construction with “of which” can sometimes make sentences appear more complex or cumbersome.
These pronouns are essential for constructing sentences that clearly and concisely convey relationships of ownership or association between different entities in a sentence.
Using “of which” illustrates a more formal or cumbersome way of indicating possession. The phrase sounds more formal and is not as commonly used in everyday speech. Using “whose” for nonhumans, as shown in the first two examples, tends to sound more natural and less formal than “of which,” which can make sentence structures appear more complex or academic.
Compound relative pronouns
Compound relative pronouns include “whoever,” “whomever,” “whichever,” and “whatever.” These pronouns combine a relative pronoun with “-ever” to add emphasis or a sense of “any” or “no matter who/which/what.” They act as subjects, or objects, or show possession within a sentence.
These sentences demonstrate how compound relative pronouns can be used to convey inclusivity or universality, referring to unspecified individuals or things in various situations.
That vs. which
In English grammar, the difference in usage between that vs. which primarily revolves around the types of relative clauses they introduce.
Note:
- “That” is used in defining relative clauses.
- “Which” is used in non-defining relative clauses.
“That” introduces clauses that define or specify the noun they modify. The information in these clauses is essential to the meaning of the sentence. If you remove it, the sentence’s meaning changes significantly.
Below, you’ll find a practice sheet with six questions about “that” and “which.” The answers along with brief explanations are on the second page of the Word document.
Who vs. that
The difference between using the relative pronouns “who” and “that” pertains to what they refer to. “Who” is specifically used for people, making sentences sound more personal. “That” is a relative pronoun often used to refer to things or animals, but it can also refer to people, especially in defining/relative clauses.
While “that” can technically refer to people, using “who” is typically preferred when the sentence is about individuals because it acknowledges the human aspect of the subject. The distinction is not a strict rule, but rather a stylistic choice that can affect the tone and clarity of a sentence.
“That” is grammatically correct in the first sentence, but can seem somewhat impersonal. The relative pronoun “who” causes the sentence to feel more directly related to the human subject. However, some readers may disagree with the use of “that” for people, so you should go with the safer choice of choosing “who.”
Who vs. whom
The difference between “who” vs. “whom” lies in their grammatical roles within a sentence structure. “Who” is used as a subject or subject complement, while “whom” is used as the object of a verb or preposition.
A simple trick to remember the difference is to try to answer the question with “he” or “him.”
Note:
- If “he” fits, use “who” (since both end in a vowel).
- If “him” fits, use “whom” (since both end with the letter “m”).
This method isn’t foolproof, especially in complex sentences or when the answer could be “they” or “them,” but it’s a good rule of thumb for quick decisions. Below, we provided a practice sheet to help you remember the difference between “who” and “whom.”
Relative pronouns and antecedents
An antecedent can be a word, phrase, or clause to which a pronoun refers or relates. In the case of relative pronouns, the antecedent is the noun or noun phrase that the relative pronoun is referring to or modifying in a sentence. The relationship between the relative pronoun and its antecedent is essential because it helps to identify which specific person, place, thing, or idea the relative clause is providing further instructions about.
Keeping the relative pronoun and its antecedent close together in a sentence is important to avoid unnecessary ambiguity. When they are separated by too many words or intervening clauses, it can become difficult to determine which noun the relative pronoun is referring to, leading to confusion about the sentence’s meaning.
In this sentence, it’s not immediately apparent which “which” refers to the library and which refers to the ceiling, creating potential confusion.
By removing the second “which” and restructuring the sentence, it becomes clear that the library has thousands of books and that the ceiling was admired by everyone due to its beautiful murals. This eliminates the ambiguity and keeps the descriptions close to their respective antecedents.
Relative pronouns and prepositions
Relative pronouns with prepositions can be a bit tricky, as the placement of the preposition depends on the formality of the context and the specific relative pronoun used. Generally, there are three cases:
- “Who/whom” with a preposition at the beginning
- “Who/whom” with a preposition at the end
- “That” with the preposition at the end
“Who/whom” + preposition at the beginning
When using “who/whom” in more formal contexts, the preposition often precedes the pronoun. This is particularly common in written English or formal speech.
“Who/whom” + preposition at the end
In informal or spoken English, it’s more common to place the preposition at the end of the clause. This is typically considered more natural in everyday conversation.
“That” + preposition at the end
The relative pronoun “that” is used in defining relative clauses, and unlike “whom,” it is used in less formal contexts where the preposition comes at the end of the clause.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
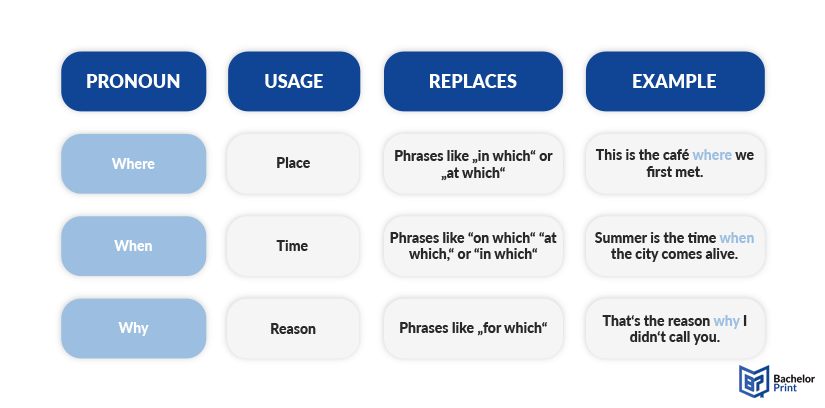
Relative pronouns in informal speech
In informal language, relative adverbs such as “where,” “when,” and “why” are often used to introduce relative clauses. These adverbs replace more formal constructions that might use a combination of a preposition and a relative pronoun (such as “in which,” “at which,” and “for which”) or to provide context related to place, time, and reason. Here’s how they are used and an example sentence for each.
Typical mistakes
When using relative pronouns, several common mistakes can occur. Understanding these errors can help in improving clarity and correctness in writing and speech.
Confusing “who” with “whom”
“Whom” should be used instead of “who” when it serves as the object of a verb or preposition.
Using “which” for people
“Who” is the correct pronoun for referring to people, not “which.”
Misplacing the preposition in formal contexts
In formal writing, the preposition should precede “whom.” However, in informal contexts, ending a sentence with a preposition is widely accepted.
Omitting the relative pronoun
While omitting the relative pronoun (“that” in this case) is common in informal speech, including it can clarify the sentence structure, especially in writing.
Using “that” instead of “who” for people
Although “that” can be used for people in informal language, “who” is more appropriate when referring specifically to individuals.
Adding unnecessary pronouns
Including an extra subject pronoun (“it” in this case) within the relative clause is a common error. The relative pronoun “which” already serves as the subject of the clause, making the additional “it” redundant.
Practice sheet
We all know the saying “practice makes perfect” and this motto also applies to the use of relative pronouns. We’ve compiled 30 practice sentences along with answers to help you understand this part of speech better. You can simply click the button and download the document.
FAQs
The seven relative pronouns are: Which, that, whose, whoever, whomever, who, and whom.
The most common ones are: Who, whom, that, and which.
- Defining/restrictive relative clauses: Necessary for understanding exactly who/what we’re talking about.
- Non-defining/non-restrictive relative clauses: Add extra, not necessary information about someone/something.
Relative pronouns are used to connect two parts of a sentence. They introduce extra information about a person, place, thing, or idea mentioned earlier in the sentence.
Imagine you have a box of toys, and you want to tell someone about a specific toy without showing it to them. You might say, “It’s the toy that lights up.” Here, “that” helps describe exactly which toy you’re talking about. These words are called relative pronouns. They help us provide additional information about someone or something in a sentence without starting a whole new sentence.
