
When working with sources, it’s crucial to ensure their credibility and reliability. The CRAAP Test—an acronym for Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose—provides a straightforward method for evaluating the quality of your sources. This guide will walk you through the steps of the CRAAP test to help you select trustworthy and appropriate sources for your research.
Definition: CRAAP test
The CRAAP test is an evaluation methodology used for evaluating the credibility and reliability of sources. The acronym CRAAP stands for Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose. By applying this method, you can decide whether a source should be utilized for your research or not. Systematically applying the CRAAP test allows you to confidently select sources that will strengthen your research and provide a solid foundation for your findings.
The 5 steps of the CRAAP test
Each step of this reliable method is explained below.
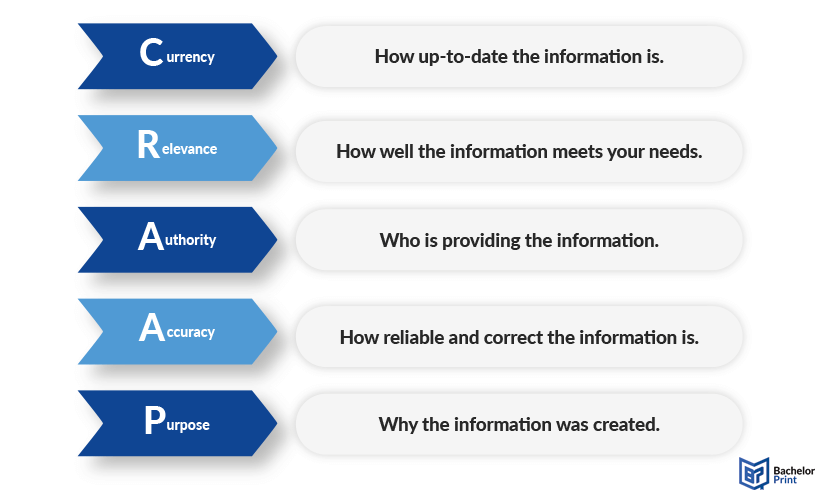

Currency
The currency ensures the information is current and relevant to your research topic. You can find it out by asking the following questions:
- When was the information published?
- Are the links functional?
- Does your topic require current information?
- Has the information been updated?

Relevance
The relevance of your source determiners if the information is significant and adds value to your understanding. This can be evaluated by asking these questions:
- Who is the intended audience?
- Does the information relate to your topic?
- Would you comfortably cite this source in your research paper?
- Is the information at an appropriate level or advanced enough?

Authority
The third step of the CRAAP test is authority and verifies the author’s credentials and expertise in the subject area. This can be identified by asking the questions below:
- Who is the author/publisher/source?
- Does the URL reveal anything about the author or source?
- Is the author qualified to write on the topic?
- Is there contact information, such as email address?

Accuracy
Accuracy checks the validity of the content. This can be found out by asking this list of questions:
- Where does the information come from?
- Are there any spelling or typographical errors?
- Does the language or tone seem without personal biases?
- Is the information supported by evidence?

Purpose
The purpose of the source can be deduced by asking these four example questions:
- Is the information fact, opinion, or propaganda?
- Does the point of view appear objective and impartial?
- Do the authors make their intensions or purpose clear?
- Are there political, cultural, or religious biases?
How to apply the CRAAP test
Below, we have created a helpful step-by-step guide on how to apply the CRAAP method when evaluating and citing sources.
- To perform the CRAAP test, begin by examining the currency of the source. Determine the publication data and assess whether the information is up-to-date and relevant to your topic. Check for any updates, revisions, or functional links that indicate the source has been maintained.
- Next, consider the relevance of the source. Ensure the information directly addresses your research question or topic by evaluating the relevance of research for your academic writing. Assess whether the content is appropriate for your audience and fits within the scope of your research.
- For the authority criterion, identify the author or organization responsible for the information. Investigate their credentials, affiliations, and expertise in the subject. Seek evidence or peer-review or editorial oversight to ensure credibility.
- Assess the accuracy of the information by cross-referencing it with other reliable sources. Check for citations, references, and evidence supporting the claims made. Be wary of any biases or unsupported statements that could undermine the reliability of the source.
- Lastly, examine the purpose of the source. Determine whether the content aims to inform, persuade, entertain, or sell. Identify any potential biases or conflicts of interest that might influence the information presented. Understanding the intended purpose helps you gauge the objectivity and trustworthiness of the source.
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
CRAAP test worksheet
A free, printable CRAAP test worksheet has been created to guide you through the evaluation of your source.
FAQs
The five questions of the acronym CRAAP are listed as follows:
Currency: The timeliness of the information.
Relevance: The importance of the information for your needs.
Authority: The source of the information.
Accuracy: The reliability, truthfulness, and correctness of the content.
Purpose: The reason the information exists.
CRAAP stands for Currency, Relevance, Authority, Accuracy, and Purpose. CRAAP test is the test used by educators and students to check the credibility and reliability of academic research sources.
The CRAAP test is used to evaluate different sources of information, including websites, books, and articles. While it is primarily used for website evaluation, it can also be applied to other sources, and even your personal knowledge can be considered in the process.
Relevance stands for the importance of the information and has an impact on the entire research. It tells you if the information relates to your topic or answers your question and if it is appropriate for your audience.
