
There are two approaches to research: inductive reasoning and deductive reasoning. Both have their benefits and drawbacks and impact numerous aspects of research. This article will discuss the deductive logical reasoning skill, its applications, and its limitations. We will also provide extensive examples. By reading this post, you will find out all you need to know about the use of deductive research.
Definition: Deductive reasoning
The meaning of deductive research is that it’s a logical approach. This methodology starts with a theory or general principle and aims to test it through the data collection and analysis of specific data. In this approach, researchers develop hypotheses based on existing theories, and then design experiments or studies to test these hypotheses. The goal is to arrive at conclusions that are logically certain, provided that the premises or starting points are true.
Deductive reasoning is mainly linked to a scientific investigation where the researcher studies what other researchers have done, examines the existing theories of the phenomenon that they’re studying, and tests the hypotheses that arise from those theories.
In this example, you started with a general theory and used it to make a specific prediction (hypothesis), which you then tested with an experiment. This is a simple example of deductive research.
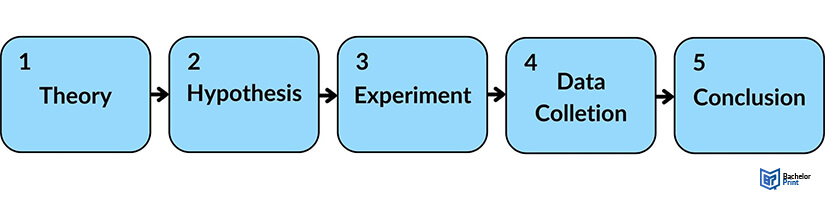
Deductive reasoning process
The process of a simple deductive logic argument generally includes four stages. There are:
- General premise or theory
- Specific premise
- Specific conclusion
- Testing or validation
Start with a general premise or theory
In the first step of deductive research, you start with a generalized statement that you assume to be true.
Adding a specific premise
Next, you go one step further and add another premise to your general theory, a more accurate statement. This should relate specifically to the situation you’re considering.
Drawing a specific conclusion
In the next step of deductive reasoning, draw a logically inevitable conclusion if the premises are true. This is being deduced from the generalized premises and specific premises.
Testing or validation
In some cases, especially in scientific research, the conclusion may be tested empirically for validity. However, with deductive reasoning, this step is not necessary as the conclusions follow logically from the premises.
In summary, our complete deductive research would look like this:
- General premise: All humans are mortal.
- Specific premise: Socrates is a human.
- Conclusion: Therefore, Socrates is mortal.
Here, the conclusion is logically certain, provided that the initial premises are true. This is basically the essence of deductive reasoning. However, errors can happen due to false premises, faulty logic, or inconsistent or irrelevant information.
Deductive reasoning examples
Deductive reasoning is a logical process where conclusions are made based on certain generalized statements or facts. It is often used in various aspects of life and fields of study to draw specific conclusions from general principles. Below are some examples that illustrate how deductive reasoning can be applied.
Mathematics
In mathematics, logical reasoning skills are fundamental to proofs and theorems. The process typically starts with established axioms or premises, and logical steps are taken to arrive at a specific conclusion.
Law
In the legal field, deductive reasoning is used to analyze evidence and testimony to establish guilt or innocence. Laws and statutes serve as the general principles, and specific cases are evaluated based on these.
Medicine
In medicine, doctors often use deductive reasoning to diagnose illnesses and prescribe treatments. For example, if a medication is known to treat a certain condition, and a patient is diagnosed with that condition, the doctor can confidently prescribe that medication.
Everyday life
In everyday situations, people use deductive reasoning for simple tasks like cooking or problem-solving. If you know that a recipe requires 20 minutes to cook at 200 °C, and your oven is set at that temperature, you can deduce that your dish will be ready in 20 minutes.
Literature and film
In literature and film, especially in genres like mystery or detective stories, characters often use deductive reasoning to solve crimes or resolve conflicts. They start with general rules about human behavior or evidence and deduce specific conclusions about whom the perpetrator might be.
These examples showcase the versatility of deductive reasoning in drawing logically sound conclusions based on accepted premises. Whether you’re solving a mathematical problem, making legal judgments, prescribing medication, or even just walking your dog, this type of reasoning leads to reliable methods for arriving at definite conclusions.
Validity and soundness
When using deductive reasoning arguments, two criteria should be considered: validity and soundness.
Validity
Validity pertains to the structural integrity of an argument. An argument is valid if, assuming its premises are true, the conclusion must also be true. The key to understanding validity is to recognize that it is about the relationship between the premises and the conclusion, not the actual truth of the statements.
Soundness
Soundness takes it a step further. A deductive argument is sound if it is both valid and its premises are true. In other words, a sound argument has a valid structure and is based on accurate information.
Relevance
When evaluating arguments, particularly in academic, philosophical, or logical discussions, it’s crucial to discern whether they’re valid and sound.
- Validity ensures that the conclusion logically follows from its premises.
- Soundness ensures that the conclusion is both logically correct and based on true premises.
Deductive reasoning in research
Deductive reasoning in research is a structured approach that starts with a general theory and seeks to test it through the collection and analysis of specific data. Below are the steps generally required for deductive reasoning, along with examples for each step.
-
Formulate a theory
A researcher might have the theory that exercise improves mental health. -
Develop a hypothesis
Based on the theory, the researcher might hypothesize that people who exercise at least 30 minutes a day will report lower levels of stress compared to those who don’t exercise. -
Operationalize variables
The researcher defines what “exercise” and “lower levels of stress” mean, possibly using metrics like duration of exercise and stress scores on a validated questionnaire. -
Design the study
The researcher might set up a controlled experiment comparing two groups of people: one that exercises for 30 minutes a day and another that doesn’t. -
Data collection
Data on exercise duration and stress levels are collected from the participants over a specified period. -
Data analysis
The researcher uses statistical methods to evaluate if there is a significant difference in reported stress levels between the two groups. -
Draw conclusions
The researcher concludes that exercising for at least 30 minutes a day significantly reduces reported stress levels, thus supporting the original hypothesis. -
Refine or adjust the theory
If the data supports the hypothesis, the theory about exercise improving mental health is strengthened. If not, the theory may need to be adjusted or refined. -
Reporting and publication
The researcher publishes the findings in a peer-reviewed journal, clearly stating whether the hypothesis was supported and discussing the implications. -
Peer review
Other researchers in the field assess the study’s methodology, findings, and conclusions, providing an additional layer of scrutiny.
By following these steps, researchers can use deductive logic to test theories in a structured and systematic way, providing valuable contributions to the body of knowledge in various academic fields.
Deductive vs. inductive reasoning
This method is often contrasted with inductive reasoning, but these are two different approaches to logic. Inductive reasoning is commonly referred to as the “bottom-up approach”, whereas deductive reasoning is commonly referred to as the “top-down approach”. This is derived from the direction of reasoning, which will be illustrated in the table below. Here, we’ll give you a quick overview of the main differences between inductive and deductive reasoning. If you want to read more about this topic, we have a separate article dedicated to these two essential approaches.
| Aspect | Deductive reasoning | Inductive reasoning |
| Direction | From general to specific | From specific to general |
| Basis | Theory or hypothesis | Observations or data |
| Certainty | Certain if premises are true | Probable, not certain |
| Use | Test theories/hypotheses | Generate theories/hypothesis |
| Example | All birds lay eggs. A sparrow is a bird. Therefore, sparrows lay eggs. | Every time I eat dairy, I feel sick. Dairy might be causing my illness |
Limitations
The problem with a deductive approach is that the conclusions can only be true and supported if all the propositions suggested by the inductive research are true and all the terms are clear.
Based on the underlying premises of deductive reasoning, the conclusion has to be true. However, if the general premise is incorrect, then the conclusion that Russians drink vodka is rendered unreliable and therefore rejected.
This is a significant weakness in deductive reasoning, since it heavily depends on the initial statement being correct. If one or more premises are incorrect, the theory is considered invalid and unsound. This has led to some critics of deductive reasoning research claiming that a deductive approach does not promote divergent thinking, and limits the scope of creativity. It assumes that every discipline in natural science will function in the same manner, yet in reality, they don’t. It’s an oversimplification.
A great application of deductive reasoning would be in weather forecasting. Meteorologists usually analyze the weather data and decide on the possible weather for that day according to their skills and judgment. They know what patterns of their initial conditions result in a specific type of weather. However, they cannot truly say that it will not rain because weather conditions can be unpredictable.
FAQs
The difference between these two approaches is that the objective of inductive research is to develop a particular theory, whereas the objective of deductive reasoning is to test that theory. Inductive reasoning, also called the “bottom-up approach”, tends to take a set of observations and then move from those experiences to wider generalizations regarding those experiences, while deductive reasoning reverses that order. However, both are reciprocally related.
Deductive reasoning is a logical process that draws specific conclusions based on general premises.
Example
- General Premise: All humans are mortal.
- Specific Premise: Socrates is a human.
- Conclusion: Socrates is mortal.
Example: Deductive reasoning
- General Premise: All birds can fly.
- Specific Premise: A penguin is a bird.
- Conclusion: A penguin can fly.
Note: This example showcases a flaw in deductive reasoning when the general premise is not entirely accurate. In reality, penguins cannot fly.
Example: Inductive Reasoning
- Observation: Every time you’ve seen a swan, it has been white.
- Conclusion: All swans are white.
Note: This conclusion might not be accurate globally, as there are black swans in places like Australia. Inductive reasoning is based on patterns and trends, but doesn’t guarantee absolute truth.
Here are five examples of deductive reasoning:
- All fruits have seeds. An apple is a fruit. An apple has seeds.
- All mammals breathe air. A dolphin is a mammal. A dolphin breathes air.
- No insects have vertebrae. A butterfly is an insect. A butterfly does not have vertebrae.
- All roses are flowers. No flowers survive without sunlight. No roses survives without sunlight.
- All planets orbit a star. Earth is a planet. Earth orbits a star (the Sun).
Deductive reasoning is like putting together a puzzle. Imagine you have the picture on the puzzle box (a general idea or rule). Using that picture, you figure out where each piece (in specific cases) should go. If you follow the picture correctly, the pieces fit together perfectly.
