Setting up an experimental methodology might seem simple at first glance, but there is more to science than dependent, independent, and control variables. Different factors can greatly influence their relationships, easily leading to research bias if they are not considered beforehand. One such type of variable is the moderator, which can strengthen or weaken the connection between variables.
Definition: Moderator variables
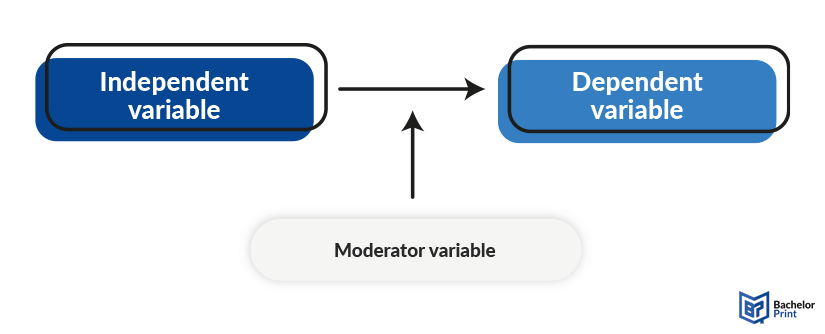
The moderator variable impacts the strength of the connection between the independent variable and the dependent variable. To ensure that a moderator variable is present, there needs to be a proven statistical interaction between the independent variable and the moderator variable.
Strength vs. direction
When it comes to the moderation of relationships between variables, you have to differentiate between the moderating variable influencing the strength and the direction of the relationship. Although every moderator variable can possibly be a categorical variable as well as a qualitative variable, there are tendencies that can hint at what kind of impact the moderator variable might have.
Strength of a relationship
Focusing on the intensity of a relationship, the moderating variable is most likely a qualitative or at least an ordinal variable. Of course, strength can also be measured as just “strong” or “weak,” but most likely, you want to figure out what impact an increase in the moderator variable has on the dependent variable.
In a case like this, it is also possible to use a nominal variable like “Do you have social support? Yes or no?” However, it is more plausible to use at least an ordinal one and focus on nuances, as social support is usually not just a “yes or no” question.
Direction of a relationship
The direction, on the other hand, is more likely to be based on a nominal variable. Since a nominal variable has logically separate outcomes, each of them might give the relationship between the independent and dependent variables another direction.
Mediator vs. moderator
The same variable can be considered a mediator as well as a moderator. The key difference is, in most cases, simply the phrasing of the research question. A mediator variable always explains a causal relationship with the lead question of “why” something happens a certain way.
A moderator investigates how the intensity of the influencing factor affects the results. The lead question is thus “how much?” It is important, when phrasing a research question like this, that the focus is still on the relationship. Be careful not to suddenly make the moderator variable an independent variable.
Moderation analysis
Y = b0 + b1x1 + b2x2 + b3(x1*x2) + ε
When determining a moderator variable in statistics, there are a few things to watch out for in a regression equation. Y is simply the dependent variable, resulting from the equation. X1 is the independent variable manipulated by the researcher, and x2 would then be the moderator. The different b’s are regression coefficients, and the ε is a standard error used to include possible errors in the calculation as a standard.
The equation now shows that if there is no moderator variable, there is still a connection between the independent and outcome variables, consisting of b0 + b1x1+ε. This is because if the moderator does not exist, x2 turns 0 and thus nullifies these factors in the equation.
The different b’s are explained as follows:
- B0 is the starting point of the regression and a constant factor. It describes the predicted value of Y when all x’s are 0.
- B1, as the coefficient of x1, describes the effect that an increase of 1 in x1 has on Y.
- B2 does the same, measuring the effect an increase of 1 on x has on Y when x1 is held constant.
- B3 represents the interaction between x1 and x2, indicating how high the influence of one is on the other.
These regression coefficients are always calculated statistically with special programs and not done by hand. The formula can also differ according to the number of influencing factors or the type of regression analysis applied in the specific situation.
Other types of variables
- Categorical variables and qualitative variables
- Quantitative variables and numerical variables
- Nominal variables
- Ordinal variables
- Discrete variables
- Continuous variables
- Interval variables and ratio variables
- Random variables
- Latent variables
- Composite variables
- Binary variables
Printing Your Thesis With BachelorPrint
- High-quality bindings with customizable embossing
- 3D live preview to check your work before ordering
- Free express delivery
Configure your binding now!
FAQs
A moderator variable influences the strength and direction of the relationship between two variables.
An example could be the relationship between offers in an online shop as the independent variable and the purchase likelihood as the dependent variable. The moderator in a case like this can be the time of day. Depending on what time it is, more or fewer people will see the offers and purchase.
The key difference between a mediator and a moderator variable is that a mediator explains the relationship between two variables, while a moderator influences its intensity.