A fundamental component in statistical tests is the methodology you employ in selecting your research variables. The careful selection of appropriate variable types can significantly enhance the robustness of your experimental design. This article explores the diverse types of variables and their classification, accentuated with various examples.
Definition: Types of variables
A variable is a trait of an item used for analysis in research. Types of variables in research are imperative, as they describe and measure places, people, ideas, or other research objects. There are many types of variables in research. Therefore, you must choose the right types of variables in research for your study.
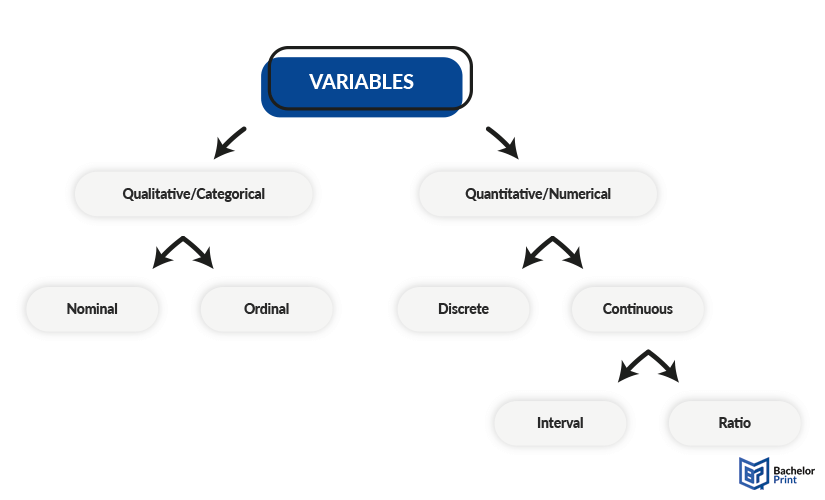
Variables can be differentiated into several categories. One way is to separate independent from dependent variables, referring to whether it is the cause or effect of something. Furthermore, types of variables can be distinguished as qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative variables can then again be defined as nominal or ordinal, while quantitative ones get separated as discrete and continuous. And eventually, there are special types of variables that belong to one of those categories.
Independent vs. dependent variables
The purpose of experiments is to determine how the variables affect each other. Therefore, you need variables you manipulate, those you keep steady to not accidentally change the conditions and those, on which you measure the effects on, called independent vs. dependent variables.
The following examples are based on a theoretical research project, which wants to investigate how the concentration of salt in water impacts the growth and survival of plants.
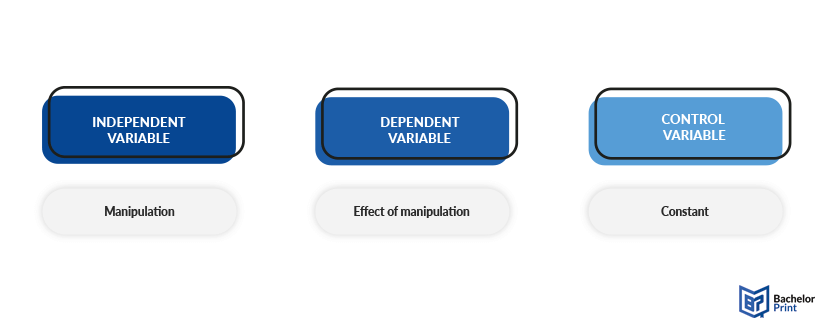
The independent variable is the one the researcher manipulates. There are various synonyms for this type of variable, including treatment variable or explanatory variable. However, the latter one mostly refers to conditions the researcher themselves cannot manually manipulate, such as the weather. If you would like to know more about explanatory vs. response variables, please follow the link to the corresponding article.
The dependent variable shows the effects of the manipulation. It is also called a response variable, as it consists of the response to the changes of the independent variable.
To make sure that the observed results are truly related to the independent variable, it is necessary to keep every other factor stable and consistent to avoid research bias. These steady factors are called control variables.
The table below summarizes all three types of variables.
| Types of variables in research | Explanation | Example (based on our example) |
| Independent variables | The variables you manipulate to affect the experiment outcome | The amount of salt added to the water |
| Dependent variables | The variable that represents the experiment outcomes | The plant’s growth or survival |
| Control variables | Variables held constant throughout the study | Temperature or light in the experiment room |
Mediator vs. moderator variables
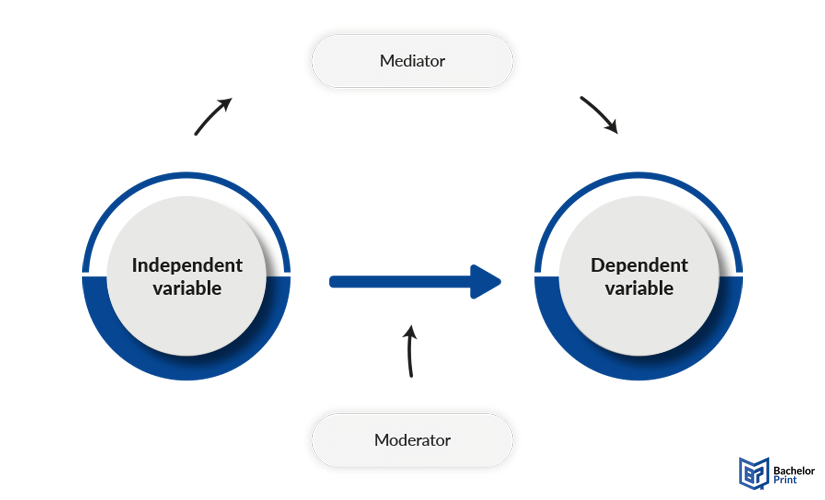
In an experiment, however, there are more than these three types of variables to be considered. Important influential factors are also mediator vs. moderator variables, which have different effects on the results of a study.
Mediator variable
A mediator variable is one that explains the connection between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is, to say it simply, the explanation for why the manipulation affects the result.
Moderator variable
A moderator variable, on the other hand, influences the manifestation of the results, whether they get stronger or weaker.
Extraneous and confounding variables
These two types of variables can involuntarily influence your study and therefore need to be eliminated. To be aware of potential bias, it is essential to look out for these.
- An extraneous variable is one, which is not considered in the experiment, but still influences the dependent variable. This can easily lead to research bias and warped results of the study. Therefore, it is important to know about the exact circumstances of your experiment and make sure that everything except for the independent variable stays consistent.
- A confounding variable is a type of extraneous variable, that influences both the dependent and the independent variable, very similar to a mediator. The difference is, however, that a mediator explains the relationship and is a logical step between the main variables, whereas the confounder is an external influence that is not meant to be researched.
Differentiating in independent, dependent, and control variables only explains what role a variable has in an experiment. To distinguish the actual types of variables, their appearances, and rules of use, we need to separate them according to different criteria. However, it is important to know that all three types above can, depending on the definition of the individual case, be sorted into the categories of the next paragraphs.
Types of variables
If you want to classify the types of variables, you can sort them into different sets, starting with the primary categories of qualitative and quantitative variables. These can then furthermore divide into subsets to specify their characteristics.
Qualitative/Categorical variables
Qualitative variables, also called categorical variables, are those represented by names or scales. They can, in some cases, also be defined by numbers. However, these numbers cannot be used in statistical calculations because they are merely simplified replacements for words. Categorical variables can be further divided into nominal and ordinal ones.
Nominal variables
Nominal variables are always single choice questions, where you usually have to select one out of two or more options. Another application would be forming categories for various purposes. The essential aspect is that the different variables do not have an order to sort them by. The simplest nominal variable is the binary variable, which consists of only two options to choose from.
Ordinal variables
Ordinal variables, on the other hand, always pose a ranking of some sort, which can either consist of numbers or labels. The important point is here that even if you use numbers for ranking, they are not empirically measurable.
Quantitative/Numerical variables
Numerical or quantitative variables hold a real value and have a mathematical meaning. Contrary to qualitative variables, these can be of statistical use in calculations. This type of variable can be differentiated into discrete and continuous ones.
Discrete variables
Discrete variables always have a distinct value, which mostly refers to whole numbers. Usually, they count occurrences, people, actions and other things that are countable.
Continuous variables
Continuous variables can take any value, such as in height, money in a bank account, time, or distances.
- Interval variables focus on the discrepancy between two data points, meaning that the margin of both is of interest. Another important criterion is that with this type of variable, 0 is a valid reference point, which can be the value of a result.
- Ratio variables, on the other hand, have an absolute zero value, meaning that 0 marks the absence of existence and data.
Special types of variables
Variables can be chosen in almost every way to suit your research, regardless of which or how many you need. There are, however, some predefined special types of variables, which will be explained in the following.
Random variables are those, whose result is based on a random event. They typically have a set of possible outcomes, out of which one of them coincidentally occurs. Mostly, they are discrete, but can in some cases also be continuous
The algebraic variables in terms are the most familiar one to students and mostly defined as x. It is used in mathematics as a space holder for an unknown value.
Binary variables are those who only have two outcomes. They can be sorted into the class of nominal variables, as the two possible results do not hold any mathematical meaning.
Latent variables cannot be measured directly, but instead need other observable variables to quantify them. They often refer to immeasurable things like satisfaction, wellbeing, or stress, where numbers cannot give exact results. You can approximate their value through ordinal values, but this is only a self-assessment of the test subject and might not be veracious.
When variables are highly related to one another, you can consider merging them into one composite variable. In many cases, composite variables are also latent variables.
Examples
The following table will give you an example for each variable in the context of academic activities.
| Type of variable | Example |
| Independent variable | Hours of studying |
| Dependent variable | Result of the exam |
| Control variable | Hours of sleep, sports activities, nutrition |
| Mediator variable | Repetition contributs to memory |
| Moderator variable | Interest in the subject |
| Extraneous variable | Test anxiety and nervousness |
| Confounding variable | Participants studied right before going to bed, leading to better remembrance |
| Qualitative/Categorical | |
| Nominal variable | Did you study? (Yes or no) |
| Ordinal variable | How confident are you to pass on a scale of 1-5? |
| Quantitative/Numerical | |
| Discrete variable | How many times did you attempt to pass this exam already? |
| Continuous variable | |
| Interval variable | The difference in credit points between your first and second attempt. |
| Ratio variable | The time needed to finish the exam, which cannot be 0 minutes. |
FAQs
The simple answer is: a lot. In a cause-effect experiment you will have the independent, dependent and control variable, as well as mediator and moderator ones. Differentiating by the characteristics of each variable, they can be divided into qualitative and quantitative ones. Qualitative variables are nominal and ordinal-scale variables, while qualitatives are discrete or continuous. The classification of different types of variables is not always easy, which is why we wrote a whole article with detailed descriptions about each one.
Mediator variables sit between independent and dependent ones and explain their relationship, while moderator variables modify the strength of that relationship or connection.
To define it, you first need to set the type of variable it has to be, give it a name and, if necessary, the values it can take. When doing research, it might also be helpful to define what the variable is not, to avoid confounding and misinterpretation.
