In today’s fast-paced digital world, printers remain essential tools for both personal and business use. Among the various types of printers available, thermal printers have carved out a niche for their speed and efficiency. From retail receipts to shipping labels, they power many everyday printing needs behind the scenes. This article explores what thermal printers are, how they work, and how they compare to other printers.
Thermal printer explained briefly
Most thermal printers use heat and pressure to print black-and-white text or images on heat-sensitive labels. This method is commonly used for barcode tags, shipping labels, and receipts.
Definition: Thermal printer
A thermal printer is a type of printer that uses a heated printhead to produce images or text on paper. Unlike traditional printers, thermal printers don’t require ink or toner. Instead, they rely on heat-sensitive printer paper or a ribbon coated with wax-like material. Thermal printing is commonly used in environments where fast, reliable, and low-maintenance printing is essential.
Printing services at BachelorPrint
- Individual solutions & personal support
- High print quality & fast production times
- Wide range of print products for every need
Learn more!
Types
In our label printer article, we’ve already scratched the surface when it comes to the two types of thermal printing: direct thermal and thermal transfer printing.
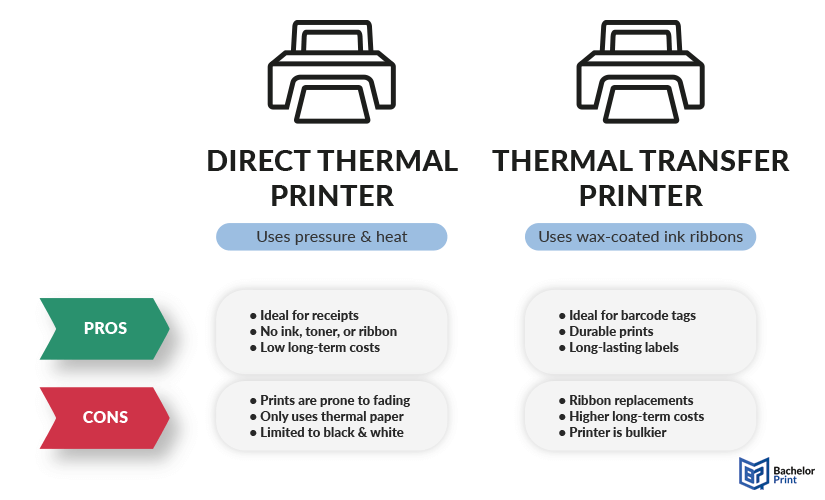
Direct thermal printer
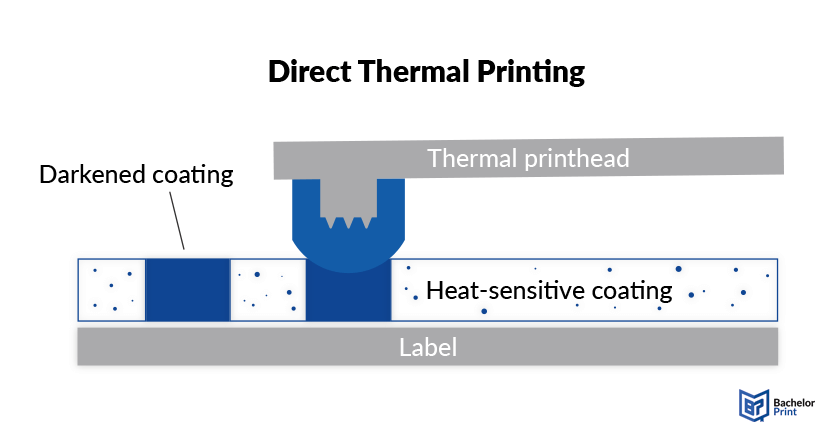
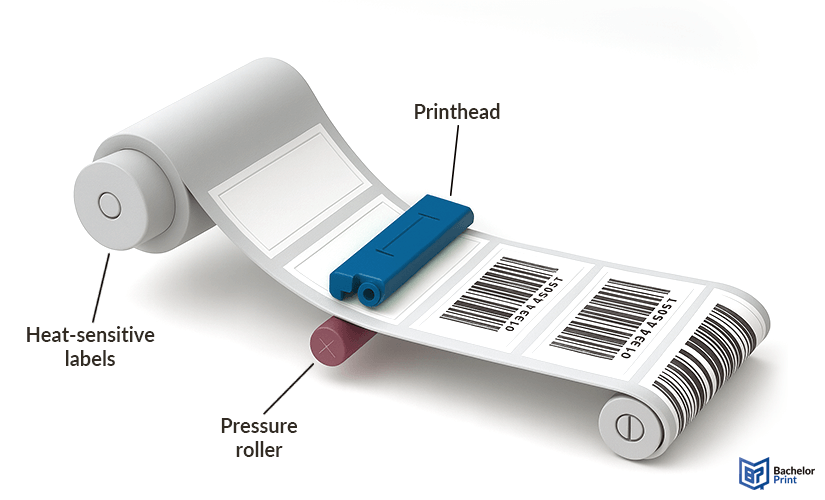
Direct thermal (DT) printers apply pressure and heat directly onto specially coated thermal paper, which darkens when it passes under the thermal printhead. As a result, the printed sheet or roll media is more sensitive to light and heat compared to other paper types and can fade if overexposed.
This is why they are typically used for short-term applications like receipts or shipping labels. The lifespan of direct thermal prints can span from 6 months to several years, depending on the environment.
Thermal transfer printer
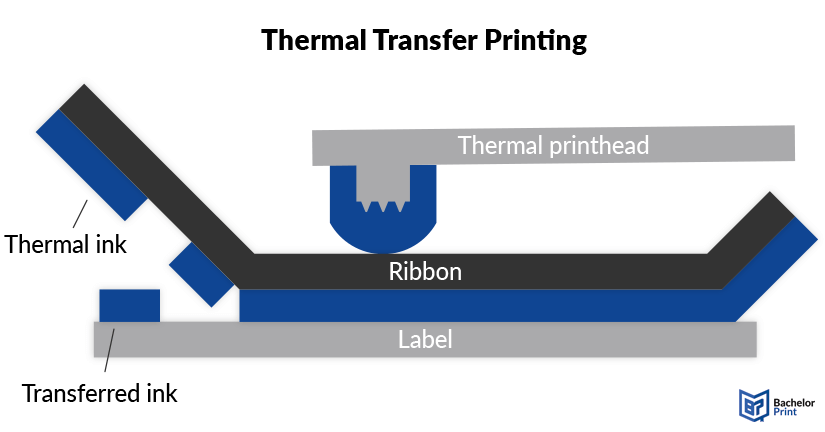
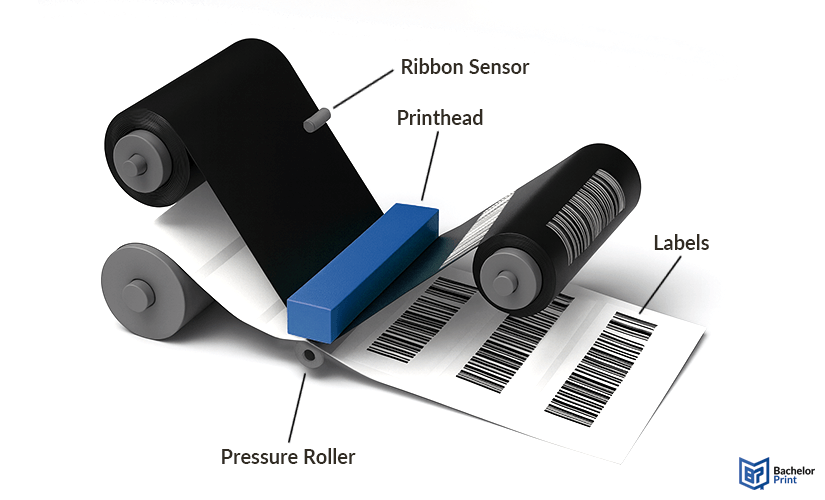
Thermal transfer (TT) printers use a wax-coated ink ribbon (or ribbons) to transfer ink onto paper or other materials using heat and pressure. The wax coating on the ribbon is melted, exposing the ink, which is then pressed against the printing material and left there to dry. This specific technique is called thermal wax printing; however, the ribbons can also be coated in resin or a mixture of wax and resin.
The result is more durable and suitable for long-term or outdoor use, such as product labels or barcode tags. For professional print quality and long durability, ribbon and label media must be compatible.
Which one should you choose?
In the image below, we’ve listed both benefits and drawbacks of each thermal printer type.
Color printing
Unlike traditional printers, thermal printers (especially portable printers) do not use printing ink. Instead, they rely on heat to produce prints. Because no ink or toner cartridges are involved, thermal printing is generally cleaner and requires less maintenance than ink-based printers.
In direct thermal printing, the heat from the printhead is applied directly to thermal paper, causing the paper to darken in specific areas. This method is used for monochrome prints, although color thermal paper can be used as a color printing alternative.
There are, however, specialized thermal printers that make color printing possible. This technology is called dye sublimation, which is also known as dye diffusion thermal transfer (D2T2) printing. These printers are equipped with a dye-coated ribbon that contains cyan, magenta, yellow, and black (CMYK) dyes. The printhead heats the ribbon ink, causing the dyes to sublimate (transition from solid to gas), and transfers onto the coated paper layer by layer.
Printer paper
The printer paper type used depends on the printing method and the intended application. Each type of thermal printer requires a compatible material to produce professional printing results.
Direct thermal printers use heat-sensitive paper that darkens when exposed to the heated printhead. It’s commonly used for:
- Receipts
- Event tickets
- Shipping labels
However, direct thermal paper is sensitive to light, heat, and friction, which can cause the print to fade over time. It’s ideal for short-term use.
Thermal transfer printers use uncoated paper or labels, along with a thermal ribbon. This method supports a wide variety of materials and is commonly used for:
- Inventory tags
- Barcode labels
- Long-lasting product labels
Interestingly, thermal printers — particularly thermal tattoo stencil printers — are widely used in the tattoo industry to create stencil transfers. Artists print tattoo outlines onto special thermal transfer paper, which is then transferred to the skin before inking.
Differences
In this section, we’ve compared thermal printers with laser and inkjet printers.
Thermal printer vs. inkjet printer
Inkjet printers are known for high-resolution images and color printing. They spray tiny droplets of liquid ink directly onto paper and can print on numerous paper types, including photo paper.
When it comes to printing, inkjets are generally slower than thermal printers and also require higher maintenance. This clears up the main differences between thermal and inkjet printers.
Thermal printer vs. laser printer
Laser printers, similar to thermal printers, don’t use printing ink; instead, they use toner cartridges and a heated drum to fuse images or text onto paper. They also have a high printing speed, which makes them ideal for bulk printing tasks.
Laser printers are usually the number one choice when it comes to document printing since they, like thermal printers, excel in creating black and white copies and prints. However, similar to inkjet printers, laser printers are higher maintenance than thermal printers.
For a comparison between inkjet and laser printers, click on the button below.
High-quality color copies from just $0.18
- Choose from different paper formats & paper weights
- Configure finishing options & add any extras you need
- Easy online ordering process with delivery to your doorstep
Learn more!
Benefits & disadvantages
Below, we’ve listed common benefits and disadvantages that come with thermal printers in general.
Pros
- Easy to use
- Compact built
- Fast printing speeds
- Ideal for logistics, DIY labels & receipts
Cons
- Limited applications
- Restricted color options
- Only usable with thermal paper
- Prints not as long-term as other printers
FAQs
A thermal printer creates images or text by applying heat to specially coated paper or a ribbon. It’s commonly used for printing receipts, shipping labels, barcodes, and other tasks.
Direct thermal printers don’t require refills; they only need thermal paper.
Thermal transfer printers do require ribbon replacements, but not ink or toner. So, while they aren’t refilled in the traditional sense, they do have consumables that must be replaced periodically.
That depends on your needs.
A thermal printer is faster, more durable, and cost-effective for high-volume tasks like labels or receipts.
An inkjet printer offers better color quality and is ideal for photo or document printing with more detailed graphics.
Five disadvantages of thermal printers are:
- Limited color options
- Sensitivity to heat and abrasion
- Special thermal paper is required
- Fading prints due to overexposure
- Direct thermal printers aren’t suitable for long-term archival