
Bookbinding is a complex procedure that requires a high amount of detail and dedication to create a satisfying result. Whether the finished product is meant to be an exclusive hardcover binding or a modern paperback, every book passes various steps before it appears in a store or bookshelf. The following article will describe every intricacy of the bookbinding process and the different parts of any physical book.
Definition: Bookbinding
Bookbinding is the process of manufacturing a book, whether done by hand or by machine. Depending on what kind of book is to be bound, hardcover or paperback, the procedure may differ in some steps. For starters, it is important to know the different components of a book, as well as the materials needed for binding.
Your guide to print and production
- Information on print finishing & print processing
- Information on materials & optimal use of materials
- Information on printing processes & print production
Learn more!
Components
Every book consists of different components, which will be listed below.
Book cover
A book cover is, by definition, the protective outer layer of any physical book. It is often illustrated appealingly to tempt customers to buy it and includes the title, occasionally a subtitle, the name of the author, and the publishing company, as well as the blurb on the back cover.


Book spine
The book spine sits in the middle of the cover, connecting the front and back (most times) on the long side. It is the place where the pages are bound and often holds information such as the title, the author, and the publishing company.
Fore edge
The fore edge is the side opposite of the spine, where the book opens. These days, you will see an increasing number of fore-edge paintings, either done by hand or by the book printing industry, adding to the charm of a book.

Text block
The text block (or book block) is the not-yet-bound stack of pages the book contains. Usually, a book block consists of several batches of folded paper instead of one pile of loose sheets.
Endpaper
Endpaper is the name of the once-folded pages that connect the book block to the cover on the inside. While it is usually just a white sheet of paper, in fantasy novels, the endpaper often includes maps of the world or even character profiles.
Types of bindings
Since books have been around for a long time, a huge number of different types of bindings have been developed all over the world. Some are quite similar, while others are so unique, you find them in only specific cultures or areas.
Tools
To bind a book, it is not only the different materials you need, but also a couple of bookbinding tools, such as a folding bone or a paper drill. If you want to know what kinds of tools you require for bookbinding, the following article will explain them to you briefly.
Materials
To bind a book, there are several bookbinding materials needed besides the book block. For the cover, especially for a hardcover, a sturdy material is needed, which is then enveloped in a type of cloth before everything gets assembled into the finished book.
Book boards
Book boards are the base of every hardcover, providing stability and protection for the book block inside. When choosing a type of book board, there are many options and materials to consider. The most common ones used are Chipboard and Bristol board.
Hardcover with individual embossing
- Price calculator & 3D live preview
- Professional binding for thesis, dissertation, or books
- Print on demand with fast delivery right to your doorstep
Learn more!
Book rebinding
Book rebinding is the process of remaking the cover of a book. These days, it is a popular hobby among readers to turn their paperbacks into beautiful and unique hardcovers, using intricate techniques to finish the cover or paint the edges of the book. Originally, it was just a process of fixing old and marred bindings by either tending the old cover or replacing it with a similar new one.
History
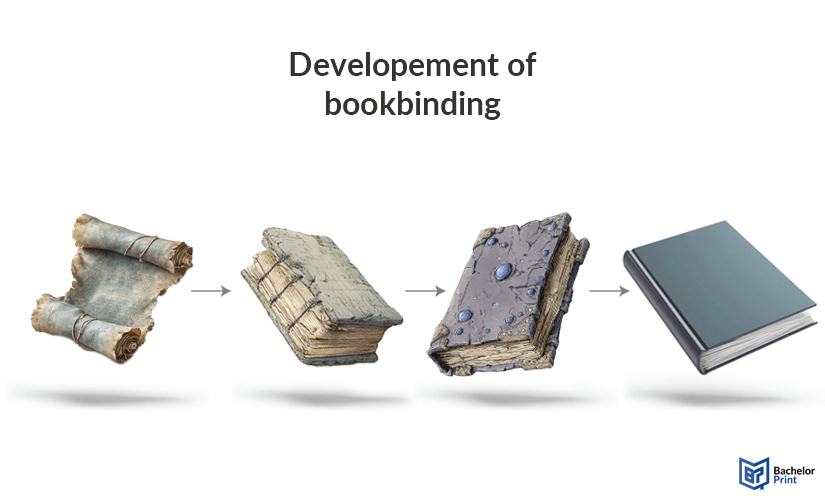
Before the concept of books was invented, the people of ancient Greece, the Romans, and other people used scrolls or wax tablets to write on. The Romans, however, also developed the first notebooks, originating from codices. A codex in the Roman sense was a sum of flat, wooden blocks attached to each other, typically illustrated with religious images, which could be folded through a hinge. Later on, paper was bound between the wooden sheets to create an ancient version of a hardcover book.
Western books from the fifth century onwards were bound as parchment between wooden boards in leather covering, often adorned with gemstones or jewelry designs. In the late Middle Ages, the art of papermaking was introduced to Europe from China, expanding possibilities of book manufacturing. With more refined techniques, the paper decreased in size and weight, allowing cheap and pocket-sized copies. Germans further developed the book printing process, especially after Johannes Gutenberg invented the printing press, making books and other paper-based documents affordable and quick to print.
Since then, a wide variety of different types of printmaking and bookbinding have been developed all around the world, leading to more types of bindings than a person might expect. If you are interested in learning about each individual possibility to bind a book, you may look at the section above, which leads to a broad overview.
Process
It takes several steps to bind a book from scratch, especially in traditional bookbinding.
- The first step of bookbinding is acquiring the book block. All the pages have to be printed, cut, and sorted in the right order.
- When using glue to bind the book, the book block is squeezed into a book press, and the left edge is sealed with glue, sticking the pages together.
In the case of traditional thread binding, an awl is used to predefine holes for the sewing process. Then the pages, usually not single but once folded in half, are sewn together with a waxed thread. - After the pages are fixed together, the book block is attached to the cover, mostly by securing the first and last page with an endpaper. Some books might also use glue to stick the block to the cover, especially when the spine is flat.
Legal and administrative foundation
Before a company can print books on a large scale or even in smaller units, there are a few factors that require thorough consideration.
- A business registration is needed to be allowed to even open a book printing business.
- ISBNs and barcodes need to be purchased for each new book published.
- Copyright laws have to be understood, especially when working with authors or translators.
- Publishing contracts have to be drafted for fair author agreements, rights deals, and royalty structures.
- Distribution rights have to be acquired either globally or regionally for the rights to print or publish digital and audio formats.
FAQs
Book binding is, simply said, the process of manufacturing a book. The procedure includes making the cover, binding the pages and attaching it altogether for a finished product.
A book always includes a book cover, a spine, the fore edge, a book block, and the endpaper.
A book block is the stack of sheets, often folded, which makes up the pages of the book. The important thing to note is that “book block” is the name only until it is bound, meaning as long as the pages are still loose.
Book rebinding refers to the process of exchanging the cover of a book and binding the pages in a new one.
To bind a book, start with the book block (the printed pages). For a hardcover, you’ll need sturdy boards, fabric for the cover, and glue or thread to attach the pages to the spine. Extras like book corners or a ribbon marker add a refined touch.