
In the context of academic research, the literature review constitutes a fundamental segment of the overarching methodology. This component is indispensable within the research process, as it facilitates a profound comprehension of the thematic focus of the scholarly paper. The literature review entails methodical scrutiny and evaluation of the extant academic literature and publications pertinent to the research question under investigation.
Definition: Literature review
A literature review (lit review) is a comprehensive synthesis of existing research and scholarly articles pertinent to a specific topic or field of study. It serves various crucial functions and poses a foundational component in academic writing, ensuring the originality and relevance of research while grounding it deeply in the scholarly field.
A literature review can be a standalone document or part of a larger academic paper, like a research paper, dissertation, or thesis, usually appearing at the beginning to set the stage for new insights. It is conducted after selecting a research topic and before primary research, helping researchers understand existing studies and identify gaps to address.
The primary purpose of a literature review is to:
- Establish a theoretical framework
- Identify research gaps
- Avoid duplication
- Provide context
- Support research design
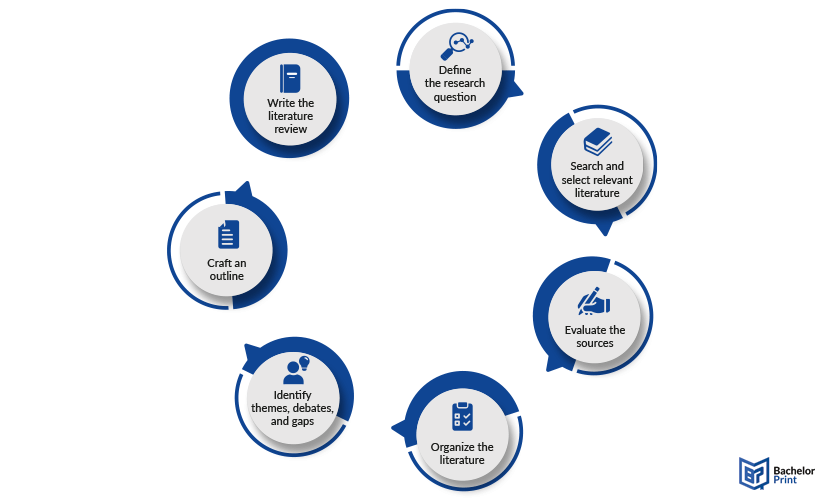
There are seven steps in total to craft a lit review successfully:
- Define the research question or topic
- Search and select relevant literature
- Evaluate the sources
- Organize and summarize the literature
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Craft an outline
- Write the literature review
Examples
Literature reviews can vary widely in their scope and depths, depending on their academic field and purpose. Each of the following examples provides a critical evaluation of the literature, noting areas where research is consistent or varies, and pointing out where further investigation is needed.
Writing a literature review
Writing a literature review is a key step in any academic research paper or project. This process helps you build a strong foundation for your own research, showing how your work fits into the bigger picture. In this guide, we’ll break down the steps to help you create a well-structured construction of the literature review.
Step 1: Define the research question
The first step in writing a literature review is to clearly define your research question or topic. This step ensures that your review is focused and relevant. A well-defined research question helps you determine what kind of literature to look for and what aspects to explore.
Step 2: Search for relevant literature
After defining your research question, start searching for relevant literature, so types of sources like journal articles, books, academic articles, and conference papers for your lit review. Apply specific keywords related to your topic to find high-quality key sources.
Start by using these keywords to find relevant sources. Below are some databases that may be useful.
- Your university’s library
- Google Scholar
- EBSCO
- JSTOR
- ProQuest
- PubMed (health, medicine, life sciences)
- PsycINFO (psychology, behavioural sciences)
- IEEE Xplore (electric engineering, computer science)
- ScienceDirect (science, technology, medical research)
- ERIC (teaching methods, pedagogy, educational research)
You can use Boolean operators to refine and focus your search. To determine if an article is relevant to your research question, read its abstract. Additionally, reviewing the bibliography of a helpful article or book can lead you to more useful sources.
Note: Make sure your search method includes a mix of older foundational studies and recent research to get a comprehensive view.
Step 3: Evaluate the sources
Once you’ve gathered a list of potential sources, evaluate them to ensure they are credible, relevant, and valuable for your research. Assess the authority of the authors, the publication date, the research methodology, and the quality of the evidence presented. Prioritize sources that are peer-reviewed and have a strong theoretical foundation.
We provide you with templates to simplify your literature review below.
Step 4: Organize the literature
Organize your literature by grouping them according to themes, trends, or methodologies to highlight the connections between sources. You can categorize the literature chronologically, by topic, or based on theoretical approaches. This structure will help you identify patterns, disagreements, and gaps in the research, making it easier to present your review in a clear and logical manner.
Start writing as you read by taking notes that can be integrated into your literature review later. Be sure to document your sources with citations to prevent plagiarism. Creating an annotated bibliography, which is a list of sources, can be useful.
Note: Include complete citation details along with a brief summary and analysis for each source. This will help you keep track of what you’ve read and save time during the writing phase.
Step 5: Identify themes, debates, and gaps
After organising your sources, analyse them to identify common themes, ongoing debates, and gaps in the existing research. Search for patterns in findings, different viewpoints on the same topic, or recurring issues that researchers disagree on. This will help you understand where your research fits in and what new contributions you can make. Additionally, pinpoint gaps—areas that haven’t been explored yet or require more research—to highlight the significance of your study.
Step 6: Craft an outline
There are multiple ways to organise the body of a literature review. You can structure it chronologically, thematically, methodologically, or based on theoretical frameworks. Depending on the length of your review, you might even combine several of these strategies. Here are the four well-known organizational patterns:
The chronological method organizes sources by their publication date, providing a timeline of how the research topic has developed over the years. It’s useful for showing the progression of ideas, trends, or changes in theories and methodologies. An example can be found above.
This organizational method organizes sources by the methods used, such as qualitative vs. quantitative research or case studies vs. experiments. It’s ideal for comparing studies that use different approaches to answer similar research questions, helping to identify methodological strengths, weaknesses, or research biases. An example can be found above.
In a thematic review, literature is grouped based on recurring central themes or topics. This helps to compare different viewpoints and analyse how different studies address the same themes. An example can be found above.
Literature is categorized based on different theoretical perspectives or models used in the studies. This organizational method is beneficial when comparing how various are applied to the same research question and which provide the most robust explanations. An example can be found above.
Step 7: Write the literature review
When writing your literature review, structure it into three main sections: introduction, body, and conclusion.
Note: If your literature review is part of a dissertation or thesis, restate your main research question and briefly summarize the academic context. You can point out why the topic is relevant now or highlight a gap. If it’s a standalone literature review, this part can be longer.
Start by briefly presenting the key topic(s) and explaining the purpose of the literature review. Include your research question or objective, and provide an overview of the organisation of your review.
Note: Show how your research fills gaps and adds new knowledge, or explain how you’ve used existing theories and methods to create a foundation for your study. If it’s a standalone literature review, this part can be longer.
Summarize the main insights from the literature review and reiterate the key themes and debates you found. Highlight any research gaps or unresolved issues that emerged from your review. Finally, explain how your own research will contribute to addressing these gaps or building on existing knowledge.
Note: The body should contain the presentation and discussion of sources, using an approach that aligns with the content and effectively conveys the findings within the review.
Organize this literature review section using the approach you’ve chosen. Here, the discussion of sources takes place. For each section, introduce the theme or category, summarize and synthesize relevant studies, compare findings, analyse and interpret how the sources relate to one another, and critically evaluate your sources. Use subheadings, transition words, and topic sentences to make the structure clear and ensure smooth connections between sections.
Below, we provided an outline for our exemplary research question.
Tips and strategies
Writing a literature review can feel overwhelming, but using the right strategies can make the process smoother and more effective. The following tips will help you stay organised , critically evaluate sources, and craft a well-structured review that adds value to your research.
-
Start with a clear focus:
Clearly define your research question to guide your search and selection of sources. -
Use Boolean operators:
You can refine your searches by using Boolean operators to find relevant literature faster. -
Stay organised :
Use reference management tools (e.g., Zotero) to keep track of sources and citations. -
Take notes and summarize:
As you read, jot down key points and summarize each source to make it easier when writing. -
Critically analyse, don’t just summarize:
Compare the strengths and weaknesses of each study and how authors approach the same topic. -
Group by themes or concepts:
Organize your review around key themes, concepts, or theories to create a logical flow. -
Be selective:
Include only directly relevant sources and contribute to your research question. -
Maintain a balanced perspective:
Present both supporting and opposing viewpoints to give a well-rounded view of the topic. -
Revise and refine:
Review your draft for clarity and coherence, and ensure it aligns with your research goals.
in Your Thesis
Checklist
A checklist can be a valuable tool to ensure your literature review is comprehensive, well-organised , and meets academic standards. Use this checklist as a guide to track your progress, from selecting sources to finalizing your review, making sure you cover all essential steps along the way.
FAQs
A literature review is a summary and critical evaluation of existing research on a specific topic. It identifies key themes, debates, and gaps, providing context for a new research study.
Before starting research for your thesis or dissertation, you need to write a review to form the context of your research within the existing knowledge. That way, you can develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your investigation.
To demonstrate your research capabilities and show that you can critically analyse information to judge its trustworthiness and value.
A literature review is a type of paper that uses research in different ways, and it essentially means finding something to say based on the gaps you identified in your study.
