
Conjunctions are parts of speech that allow you to connect two or more thoughts. In academic writing, coordinating conjunctions do not only connect words, phrases, or sentences, they can also stand at the start of a sentence or phrase. In this article we’ll discuss coordinating conjunctions, the different rules in specific cases, and how they differ from conjunctive adverbs.
Definition: Coordinating conjunction
Coordinating conjunctions connect two clauses or ideas of equal grammatical and syntactic importance. For instance, these conjunctions can join two verbs, nouns, adjectives, phrases, or independent clauses but can never start sentences. The seven coordinating conjunctions are also referred to by the acronym “FANBOYS.”
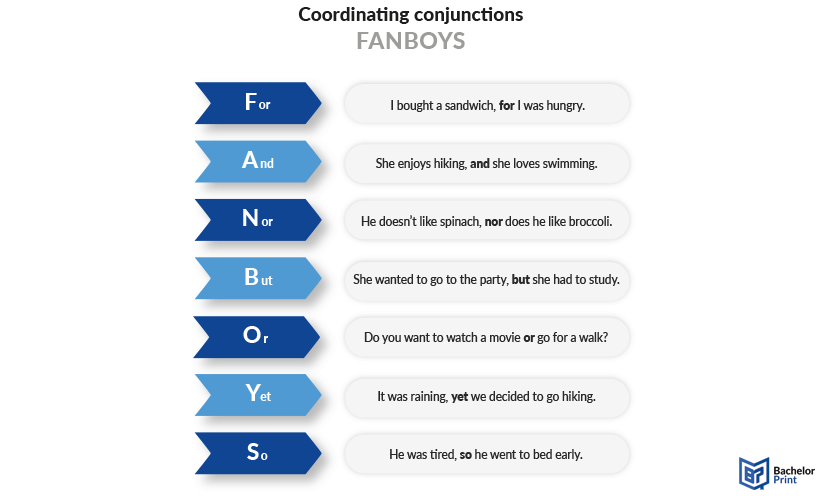
The 7 coordinating conjunctions
There are seven main coordinating conjunctions in English. Each conjunction has a specific function. Therefore, memorizing all of them and how you can use them is essential in academic writing. The seven types are:
“For” is one of the most common conjunctions in the English language. Many people use this conjunction without recognising what part of speech it is. This conjunction indicates that one part of a sentence occurred because of the other one. “For” is also a preposition; therefore, you should be keen about how you use it in your sentences.
“And” is not only one of the most common words in English but also one of its most frequently used conjunctions. This conjunction helps connect two words that occur equally or with equal significance. As illustrated by the examples below, “and” can connect many words, such as verbs, nouns, adjectives, phrases, or adverbs. It can also connect general ideas as seen in the examples below.
Th conjunction “nor” is used when combining one negative statement with another. It can only come after a negation word.
The conjunction “but” contrasts or differentiates an idea from another; however, the second idea is surprising or changes direction.
“Or” expresses an alternative in a sentence. It is one of the simplest conjunctions to use.
This conjunction contrasts the first idea in the sentence and the one after the conjunction. Also, you can use “yet” the same way you use “but”; however, “yet” demonstrates that the contrasting idea may occur in the future.
Comma rules
When it comes to comma rules with FANBOYS, there are some specific rules. If you’d like to find out more about this, click on the button below.
Coordinating conjunctions vs. conjunctive adverbs
We have compared both below.
Coordinating conjunctions
They connect two equal grammatical elements.
Conjunctive adverbs
They show ties between two independent clauses.
- ✓ Free express delivery
- ✓ Individual embossing
- ✓ Selection of high-quality bindings
FAQs
The seven coordinating conjunctions are referred to as FANBOYS: For, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so.
Five examples are:
- I wanted to go for a walk, but it started raining.
- She plays the guitar and sings beautifully.
- We can watch a movie, or we can go bowling.
- He didn’t learn, so he did it again.
- They didn’t call, nor did they text.
A coordinating conjunction is a word that joins two or more equal parts of a sentence.
While coordinating conjunctions simply connect two equal grammatical elements, conjunctive adverbs show relationships between two independent clauses.