
Understanding tenses is crucial for mastering any language, as they form the backbone of how we express time in communication. One of the fundamental tenses in English is the past simple, a key component of our language rules. The past simple tense is used to describe actions or events that occurred at a specific time in the past. In this article, we will explore the rules and usage of this tense, shedding light on how to form and apply it correctly in various contexts.
Definition: Past simple
The past simple (also: simple past) tense is a verb tense used to indicate that an action or situation occurred in the past and is now finished. This tense does not indicate whether the action was completed recently or a long time ago, just that it is not ongoing. With the active voice of past simple, there are no auxiliary verbs or participles needed, unlike other tenses such as the present perfect tense, making its usage straightforward. You simply use the past form by adding “-ed” to regular verbs, while irregular verbs have unique conjugations that must be memorized. Simple past is used to describe completed actions in the past, to recount events in a narrative, or to express actions that happened at a specific time in the past, even if the time is not mentioned.
Formula of past simple active voice
The past simple tense is a foundational aspect of English grammar. This tense is characterized by its straightforward structure, relying solely on the base form (infinitive) of verbs. Unlike with present simple, you don’t need to take pronouns or subject-verb agreement into account, as all verbs in past tense maintain the same form. One exception to this rule, however, is the past form of “to be,” which changes to “was/were.” In this section, we will explore the rules and patterns involved in creating the past tense for both regular and irregular verbs by providing clear examples and explanations.
Regular verbs
Regular verbs adhere to a predictable conjugation pattern. Typically, they form their past tense by adding “-ed” to the infinitive. However, there are some regular verbs with specific spelling changes:
- If the verb ends in a consonant, it sometimes gets doubled before adding -ed.
- If the verb ends in -y and a vowel doesn’t precede it, we change it to an -i before adding -ed.
- If the verb ends in -e, we only need to add -d to the base form.
| Infinitive | Past simple |
| To walk | walked |
| To play | played |
| To plan | planned |
| To stop | stopped |
| To cry | cried |
| To marry | married |
| To dance | danced |
| To love | loved |
Irregular verbs
The English language contains approximately 200 irregular verbs that do not conform to standard conjugation patterns. These verbs have distinctive forms for different tenses, often exhibiting unpredictable changes in spelling or pronunciation between the infinitive, past tense, and past participle. The past participle is one of the two past forms and is used in forming perfect and passive tenses. Irregular verbs can be divided into four different categories:
- Verbs with a different infinitive, past simple, and past participle.
- Verbs with the same infinitive, past simple, and past participle.
- Verbs with only the same past simple and past participle.
- Verbs with only the same infinitive and past participle.
| Infinitive | Past simple | Past participle |
| To be | was/were | been |
| To buy | bought | bought |
| To come | came | come |
| To do | did | done |
| To fly | flew | flown |
| To go | went | gone |
| To hurt | hurt | hurt |
| To lie | lay | lain |
To enhance your understanding, we have created a PDF document that encompasses both regular and irregular verbs, which you may obtain by downloading it from the link provided below.
Practice worksheet
Now that you know how to form the past simple tense, it is time to practice its conjugations. Below, you can find ten example sentences that include both regular and irregular verbs in various contexts in the past. Let’s see if you can get them all correct.
- She _____ to the shop and _____ some groceries. (To walk, to buy)
- They _____ football yesterday and _____ the match. (To play, to win)
- He _____ for the exam and _____ confident about his answers. (To study, to feel)
- We _____ the museum and _____ many interesting exhibits. (To visit, to see)
- I _____ my room and _____ an old photo album. (To clean, to find)
- She _____ her friend with homework and _____ a letter. (To help, to write)
- They _____ a film and _____. (To watch, to eat)
- He _____ the car and _____ it to work. (To fix, to drive)
- We _____ the house and _____ a new fence. (To paint, to build)
- I _____ at the joke and _____ around the garden. (To laugh, to run)
- She walked to the shop and bought some groceries. (To walk, to buy)
- They played football yesterday and won the match. (To play, to win)
- He studied for the exam and felt confident about his answers. (To study, to feel)
- We visited the museum and saw many interesting exhibits. (To visit, to see)
- I cleaned my room and found an old photo album. (To clean, to find)
- She helped her friend with homework and wrote a letter. (To help, to write)
- They watched a film and ate. (To watch, to eat)
- He fixed the car and drove it to work. (To fix, to drive)
- We painted the house and built a new fence. (To paint, to build)
- I laughed at the joke and ran around the garden. (To laugh, to run)
Active question form of past simple
To form questions in the past simple tense, we use the auxiliary verb “did,” which is the past form of “do,” followed by the subject, the base form of the main verb, and of course a question mark.
Structure
Did + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Questions with question words
While most questions in the past simple tense use “did,” there are exceptions, particularly when “who,” “what,” or “which” are subjects of the sentence. In this case, “did” can be omitted, meaning the verb needs to be in its past form again.
Negative question form of past simple
Negative questions in the past simple tense can be formed in two ways:
- Using the contraction “didn’t.”
- Inverting the subject and auxiliary verb “did,” and adding “not.”
Structure
Didn’t + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Did + subject + not + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
The first question form of past simple with the apostrophe is more commonly used in spoken English and in informal writing. It often implies slight surprise or seeks confirmation of something the speaker expects to be true or is unsure about.
The second question form of past simple tends to be more formal and is more commonly found in written English. It places a clearer emphasis on the negative aspect, often used to express disbelief or surprise.
Negative questions with question words
When forming negative questions with question words (who, what, where, etc.) in the past simple tense, the structure includes “did not” or “didn’t.”
Structure
Question word + didn’t + subject + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
Question word + did + subject + not + infinitive + rest of the sentence?
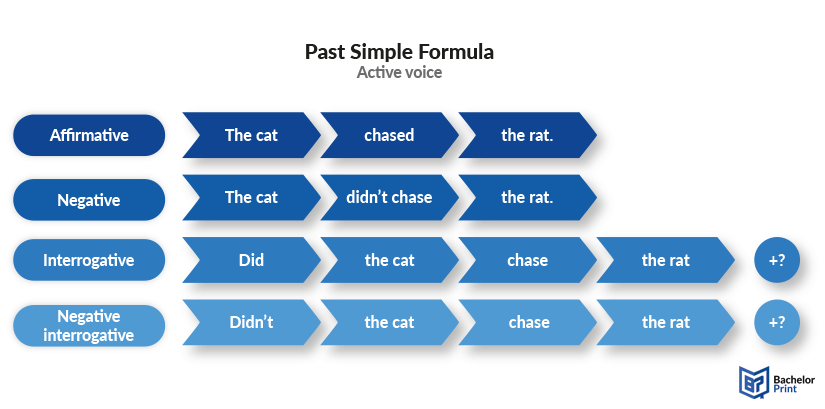
Below, we have created an image that illustrates the structures of the past simple active voice.
Formula of past simple passive voice
As we’ve gone through the structure of simple past’s active voice in the previous paragraphs, it’s now time to talk about the structure of the passive voice. It is used when the focus is on the action rather than the subject performing the action. It is formed by using the auxiliary verb “was/were” and the past participle of the main verb. When people are involved, we use the agent “by” to show the doer of the action. The object in an active sentence becomes the subject of the passive sentence.
Structure
Subject + was/were + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Subject + was/were + not + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
or
Subject + wasn’t/weren’t + past participle (+ by agent) + object.
Structure
Was/Were + subject + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
Structure
Was/Were + subject + not + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
or
Wasn’t/Weren’t + subject + past participle (+ by agent) + object?
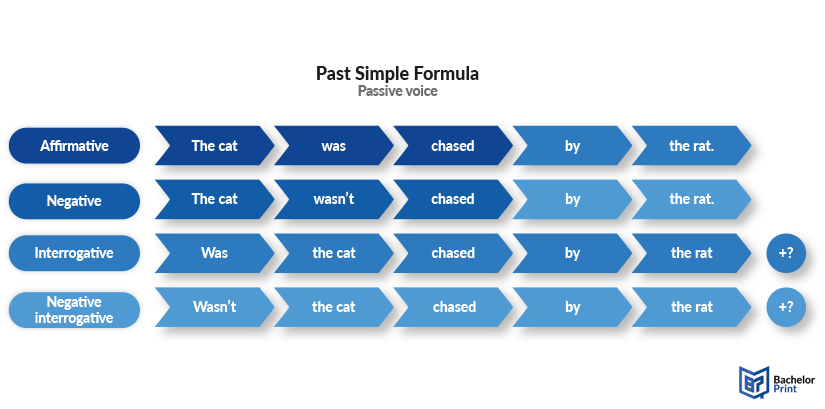
Below, we have created an image to summarize the form of the past simple passive voice.
Indicators for past simple
There are numerous tenses in the English language, but for each one, there are time expressions that make it easier to figure out which past tense to use. Here are some common indicators for the past simple tense, along with examples.
Yesterday
Refers to the day before today.
Last night/week/month/year
Refers to the previous night/week/month/year.
In [year]
Refers to a specific year in the past.
[Number] days/weeks/months/years ago
Refers to a specific number of day/weeks/months/years before the present.
On Monday/Tuesday/etc.
Refers to a specific day of the week in the past.
On [date]
Refers to a specific date in the past.
The other day
Refers to a recent day, not specified exactly.
Once
Refers to a single time in the past.
When
Used to describe a time in the past.
During
Refers to a specific full stop or event that was completed within that full stop.
- ✓ 3D live preview of your individual configuration
- ✓ Free express delivery for every single purchase
- ✓ Top-notch bindings with customised embossing

Short answers in past simple
Short answers in the past simple tense are concise responses that confirm or deny the occurrence of an action. They can be used in both active voice with “did” or “didn’t” and in passive voice with the auxiliary verbs “was/were” or “wasn’t/weren’t.” Here’s how to form short answers in past simple, along with examples.
Active voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + did.
Negative: No, + subject + didn’t/did not.
Passive voice
Structure
Affirmative: Yes, + subject + was/were.
Negative: No, + subject + wasn’t/weren’t.
Practice exercise
To conclude this article, you can test your knowledge of past simple with this practice exercise. The answers for the correct past simple conjugations can be found in the second tab. Learning English tenses can be difficult, specifically irregular verbs, so don’t get frustrated when you can’t get a perfect result. As they say in the English proverb, “Rome wasn’t built in a day,” meaning that achieving great things takes time and effort.
- She ____ the house yesterday. (To clean, active)
- He ____ a letter to his friend. (To write, active)
- They ____ ____ the film last night. (To watch, negative)
- I ____ ____ to the gym this morning. (To go, negative)
- ____ she ____ her homework? (To finish, interrogative)
- ____ you ____ the latest episode of the show? (To see, interrogative)
- ____ they ____ you last night? (To call, negative interrogative)
- ____ he ____ the documents? (To bring, negative interrogative)
- The book ____ ____by millions of people. (To read, passive)
- The cake ____ ____ by Melanie. (To bake, passive, negative)
- She cleaned the house yesterday. (To clean, active)
- He wrote a letter to his friend. (To write, active)
- They didn’t watch the film last night. (To watch, negative)
- I didn’t go to the gym this morning. (To go, negative)
- Did she finish her homework? (To finish, interrogative)
- Did you see the latest episode of the show? (To see, interrogative)
- Didn’t they call you last night? (To call, negative interrogative)
- Didn’t he bring the documents? (To bring, negative interrogative)
- The book was read by millions of people. (To read, passive)
- The cake wasn’t baked by Melanie. (To bake, passive, negative)
FAQs
A past simple example is a sentence that describes an action or event that was completed in the past.
Example
- She walked to the shop.
The simple past, also known as the past simple tense, is used to describe actions or events that were completed at a definite time in the past. This tense indicates that the action is finished and no longer happening.
- She cleaned the house yesterday.
- He wrote a letter to his friend.
- They watched a film last night.
- I went to the gym this morning.
- We visited the museum last week.
- She cooked dinner for her family.
- He finished his homework.
- They travelled to Spain last summer.
- I met my friend for lunch.
- She bought a new dress.
The past simple form of a verb is created in two main ways:
- Regular verbs: Add “-ed” to the base form of the verb.
Walk ⇾ walked
- Irregular verbs: Change the verb to a specific past form, which must be memorized.
Go ⇾ went
Indicators of the past simple tense include: yesterday, last night/week/month/year, in [year], on Monday/Tuesday/etc., once, when, during, on [date], the other day, and [number] days/weeks/months/years ago.
