There are many different types of variables to use in methodology. It is essential to know their differences in order to use them correctly. Besides the simpler categorical variables, there are also quantitative variables, which hold measurable value. These are most important for academic studies of any kind, and thus for your thesis. The following article will dive into the depth of this variable, its subtypes, and its use.
Definition: Quantitative variables
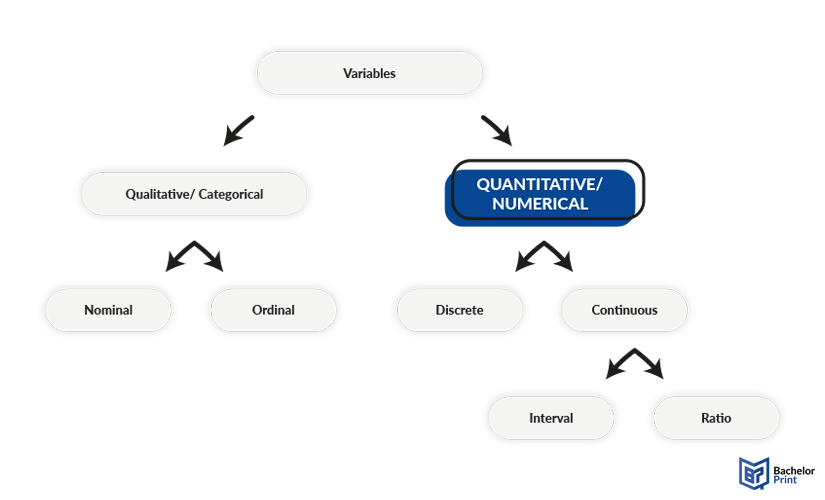
Quantitative variables can also be called numerical variables, as their value is defined by measurable magnitudes. The numeric results from an experiment or study can be of statistical use and valid in comparisons. There are two subtypes of quantitative variables: discrete and continuous ones. Discrete variables can only assume a value of whole, countable numbers, such as people, objects, or credit points in exams. Continuous variables can be considered a steady line with uncountable subsequent values, such as height, time, and temperature.
Discrete variables
Discrete variables are a type of numeric variable that take on countable numbers, meaning only integers and no decimals.
Continuous variables
Continuous variables, on the other hand, can have individually long decimals as they can be split into smaller and smaller units. Furthermore, this type of quantitative variable can be divided into interval variables and ratio variables, depending on whether 0 is a valid reference point or not. Reference point, in this case, describes whether it can be considered a valid outcome of a calculation or not.
Interval Variables
Interval variables have 0 as a valid reference point, meaning that the value zero holds meaning and can be a valid outcome of a calculation.
Ratio Variables
Ratio variables do not have 0 as a reference point. Zero in ratio variables simply indicates nonexistence and is not a valid outcome of calculations.
Identification
Identifying whether a variable is quantitative or not is rather simple, as the following steps show.
-
- Is the variable given as words (yes/no; green/blue/red) or as numbers?
→ Words indicate it is a categorical variable (especially nominal). - Do the variables hold mathematical meaning?
→ Ordinal variables ask for ratings (e.g., a scale from 1 to 10). - Do the variables consist of decimals or not?
→ No decimals indicate discrete variables.
→ Decimals indicate continuous variables. - Is 0 a valid result for calculation with these variables?
→ E.g., 0 meters is a valid result → interval variable.
→ E.g., an age of 0 is invalid → ratio variable.
- Is the variable given as words (yes/no; green/blue/red) or as numbers?
Applications
The use of numerical variables is mostly only a matter of what you are measuring and how you phrase your research question. If you phrase a question with a multiple-choice answer system, then you are using a nominal variable; if your question asks to pick from a scale, it is an ordinal variable.
However, if your question asks for a specific number of something, like the number of days spent on holiday or the production units of a company per year, you are measuring a quantitative variable. These last two examples refer to a discrete variable, while applications of a continuous variable could be the time spent studying or the weight of different items.
Other types of variables
- categorical variables and qualitative variables
- quantitative variables and numerical variables
- nominal variables
- ordinal variables
- discrete variables
- continuous variables
- interval variables and ratio variables
- random variables
- latent variables
- composite variables
- binary variables
- ✓ 3D live preview of your individual configuration
- ✓ Free express delivery for every single purchase
- ✓ Top-notch bindings with customised embossing

FAQs
Quantitative variables are defined by their trait of being measurable. They can be split into two subcategories: discrete and continuous.
Examples of discrete variables: goals scored in a match, days absent from work.
Examples of continuous variables: money in a bank account, weight.
Quantitative or numeric variables are those, who have an arbitrary high number of countable values. This means that, opposite to categorical variables, whose values are determined in a set beforehand, there is no limit to the number of possible outcomes and the only condition is that the values need to be wholes. Such as people, objects, days, etc.
No. It is important to not confuse the terms qualitative and quantitative. A numeric variable is the same as a quantitative variable, which is defined by having values in measurable amounts. Qualitative variables are also called categorical variables and are characterized by their feature to have only a fixed set of non-numerical values.
Discrete variables consist of only integral numbers, as they count only wholes, such as people, objects, whole days, etc. Continuous variables on the other hand, can have any decimal length.