You have probably seen the term RGB on products, such as keyboards, monitors, or LED lights. However, it is more than just colorful backlighting. Behind those glowing effects lies the RGB color model, the foundation for how every screen displays color. Understanding it is essential if you’re preparing digital files for printing, since what you see on screen looks different on paper.
RGB explained briefly
RGB (Red, Green, Blue) is an additive color model used for digital displays, where colors are created by combining light. Thus, RGB is not suitable for printing, so files often need conversion to a print-ready color space (like CMYK) to maintain color accuracy.
Definition: RGB
RGB stands for red, green, and blue, the three primary colors of light that form the basis of the RGB color system. It’s an additive color model, meaning colors are created by combining light rather than mixing pigments.
When these three colors of light overlap in different intensities, they produce the entire spectrum of visible colors. For instance, red and green light together create yellow, blue and green make cyan, and all three at full strength form white.
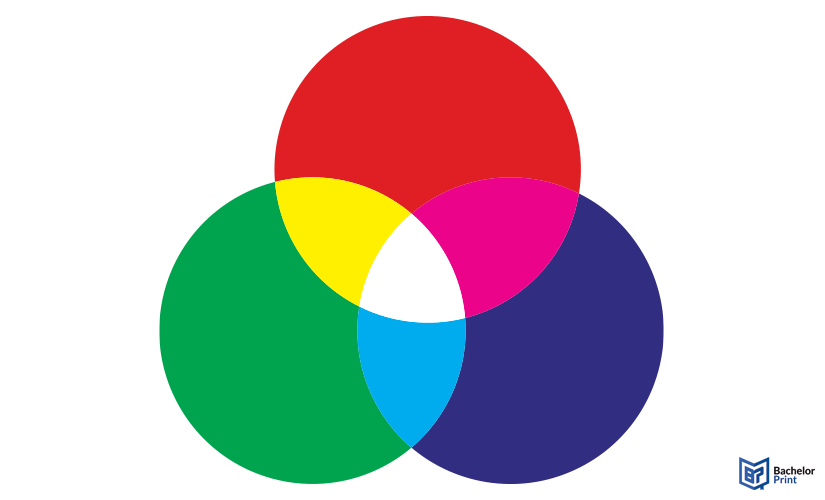
This principle is used in all light-emitting or light-capturing devices to display images accurately.
In contrast, print colors work differently. They follow the subtractive CMYK model, where printing inks absorb light instead of emitting it.
How the RGB model works
The RGB model is based on additive color mixing, where colors are created by adding light rather than applying pigments. Each of the three light sources contributes to the final color seen on a screen. By varying their intensity, millions of different hues can be produced.
This principle differs from the subtractive color model used in printing, such as CMYK, in which inks absorb light rather than emit it.
PDF printing at BachelorPrint from CAN$0.14
- Upload your files & order printed PDFs in minutes
- Secure online PDF printing service with reliable delivery
- High-quality prints from any PDF, including reports & more
Learn more!
Most popular RGB codes
Here are the most searched RGB color codes worldwide:
Color name
RGB value
Hex code
Black
RGB(0, 0, 0)
#000000
Blue
RGB(0, 0, 255)
#0000FF
Cream
RGB(255, 253, 208)
#FFFDD0
Dark Blue
RGB(0, 0, 139)
#00008B
Dark Brown
RGB(101, 67, 33)
#654321
Dark Green
RGB(0, 100, 0)
#006400
Gold
RGB(255, 215, 0)
#FFD700
Gray
RGB(128, 128, 128)
#808080
Green
RGB(0, 128, 0)
#008000
Hot Pink
RGB(255, 105, 180)
#FF69B4
Light Blue
RGB(173, 216, 230)
#ADD8E6
Light Gray
RGB(211, 211, 211)
#D3D3D3
Magenta
RGB(255, 0, 255)
#FF00FF
Maroon
RGB(128, 0, 0)
#800000
Navy Blue
RGB(0, 0, 128)
#000080
Purple
RGB(128, 0, 128)
#800080
Tan
RGB(210, 180, 140)
#D2B48C
Teal
RGB(0, 128, 128)
#008080
White
RGB(255, 255, 255)
#FFFFFF
Yellow
RGB(255, 255, 0)
#FFFF00
RGB vs. CMYK
While RGB defines how colors appear on screens, CMYK determines how those same colors are reproduced on paper. Both are essential color models, but they work in entirely different ways.
RGB
CMYK
Purpose
Digital displays & online content
Printing on physical materials
Color system
Additive
➜ Colors are created by adding lightSubtractive
➜ Colors are created by combining inks
Primary colors
Red, green, blue
Cyan, magenta, yellow, key (black)
Medium
Screens, cameras, projectors
Printers, presses, printed media
Color range (gamut)
Wider
➜ Can display more vibrant tonesNarrower
➜ Some RGB colors can’t be reproduced
Output result
Luminous and bright on screen
Matte or saturated, depending on paper and ink
Before printing, images created in RGB must be converted to CMYK to accurately reproduce colors with ink. Otherwise, the final print may look slightly different or less vibrant than on screen.
Designers usually edit and proof their files, using tools such as color correction, ICC profiles, and soft proofing to ensure the on-screen colors translate as closely as possible to print. Because RGB covers a wider color gamut than CMYK, some bright tones can’t be matched exactly on paper.
Note: In CMYK, the “K” stands for “key,” referring to black ink. It’s named “key” because it’s the key color plate that defines sharpness and alignment in the final print.
Color values & hex codes
In digital design, RGB values are often written in hexadecimal format (also called hex codes). Each pair of digits represents the red, green, and blue values in hexadecimal notation.

Here is our BachelorPrint Blue in hex code:

Hex codes are especially common in web and digital design, where they make it easy to define exact colors in coding languages. Tools such as Figma, Adobe Photoshop, and Illustrator support both RGB and hex formats, allowing designers to keep colors consistent across screens and when exporting files for web use.
Color spaces based on RGB
Not all RGB colors are created equal, because different devices interpret them slightly differently. That’s why there are several color spaces, each defining a specific range (gamut) of colors and how they’re displayed.
Common RGB color spaces
The standard color space for most screens and the web. It offers reliable, consistent color display across devices, which makes it ideal for online content.
Has a wider color gamut than sRGB, especially in greens and blues. It’s preferred for photo editing and print preparation, since it retains more detail before converting to CMYK.
Covers an even larger gamut, beyond what most screens can display. It’s mainly used by professional photographers who need the highest color accuracy in post-production.
Tips for working with RGB
These quick tips make color management easier and help avoid surprises during printing:
✅ Always verify whether your file is set to RGB or CMYK before sending it to print.
✅ A well-calibrated screen ensures colors appear as accurately as possible when editing.
✅ Apply the correct ICC profile for your printer and paper type to achieve consistent results.
✅ Activate a CMYK preview in your design software to simulate how colors will look when printed.
✅ BachelorPrint’s live preview feature lets you see exactly how your uploaded file will appear before it’s printed, helping you spot any color issues early.
Dissertation or thesis printing and binding
- Fast production & express delivery to meet your deadline
- Professional thesis & dissertation printing & binding services
- Premium materials, hard & soft bindings for a lasting impression
Learn more!
FAQs
Neither is “better” because they serve different purposes.
- RGB is ideal for digital screens
- CYMK is used for print colors
RGB stands for red, green, and blue.
Humans perceive color in a way that’s closer to RGB, because our eyes have receptors sensitive to red, green, and blue light. The RYB model (red, yellow, blue) is mainly used in traditional art and paint mixing, not in digital color representation.
The RGB color system can create millions of shades by combining red, green, and blue light at different intensities. Nearly every color visible on screen is made this way.
Each color value (0–255) defines how much of each light color is used.
Examples
- RGB (0,0,0) is black
- RGB (255,255,255) is white
- RGB (255,0,0) is full red with no green or blue